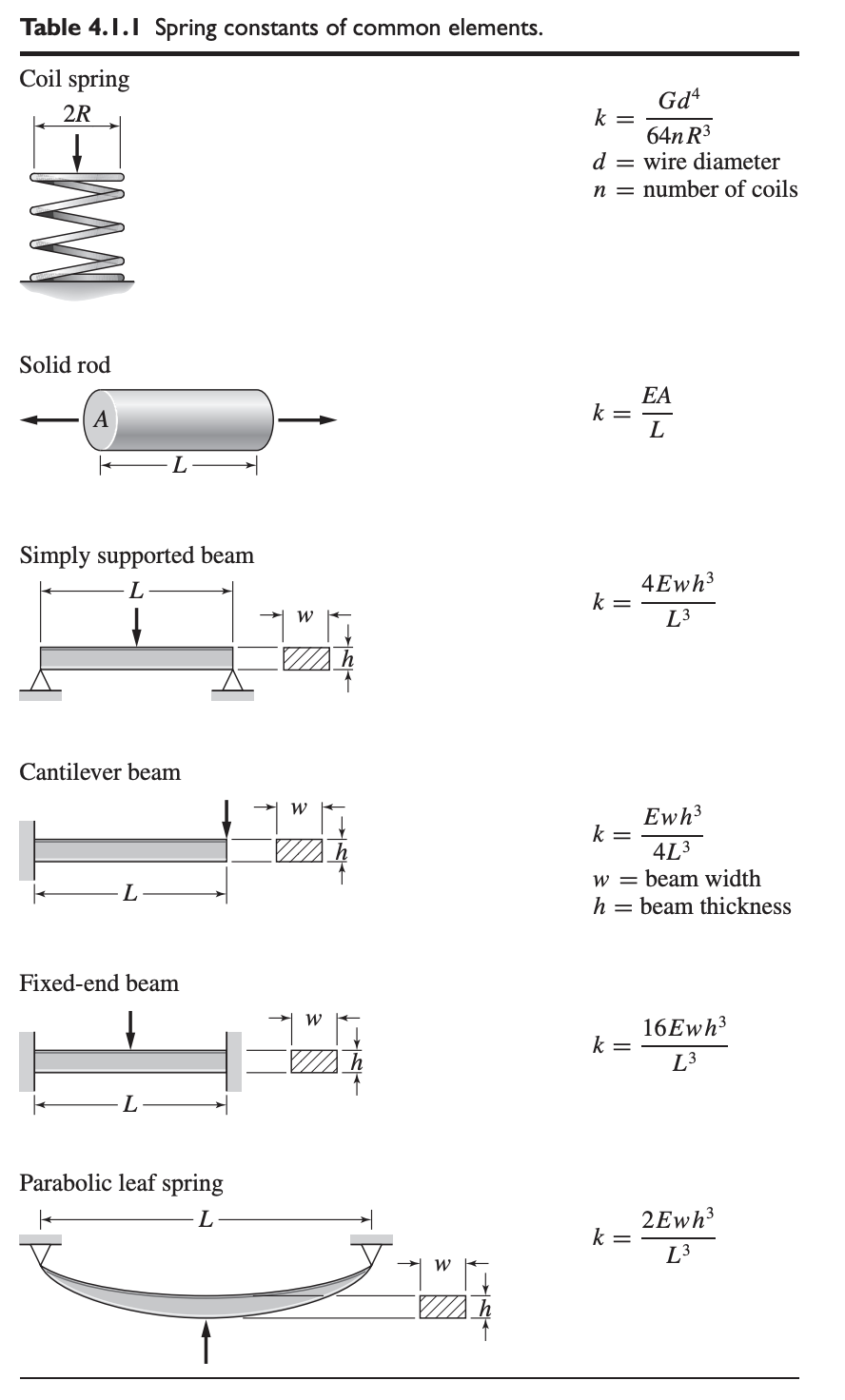
Spring elements are physical objects whose deformation under forces cannot be treated as negligible.
Coil Spring
A translatory or coil spring has a free length, . When a spring is compressed or stretched, it exerts a restoring force that opposes the compression or extension. This can be examined under the linear force-deflection model:
where is the restoring force, is the compression or extension distance (change in length from free length), and is the spring constant. This is also known as Hooke’s Law.
Torsional Spring
A torsional spring refers to an element that resists with an opposing torque when twisted. This behavior is expressed by:
where is the net angular twist in the element, is the torque causing the twist, and is the torsional spring constant. We say is the spring position where there is no torque; this is analogous to the free length.
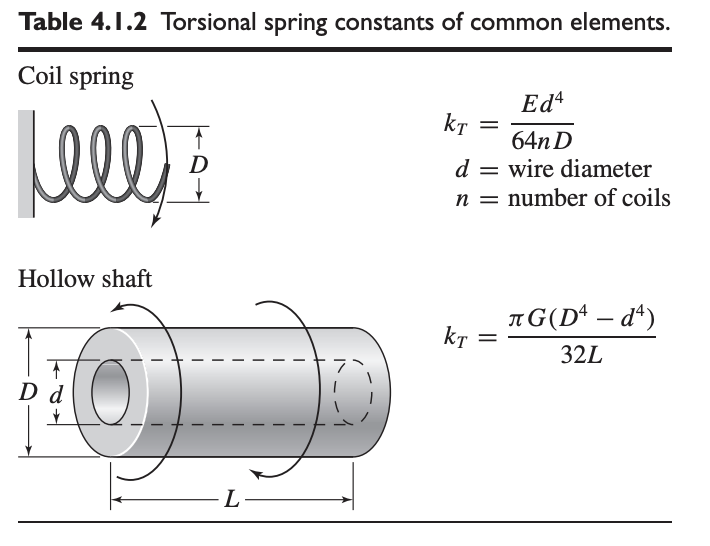
The methods of calculation for the torsional spring constant is shown above.
Spring Constants