A mass-spring system is shown below:
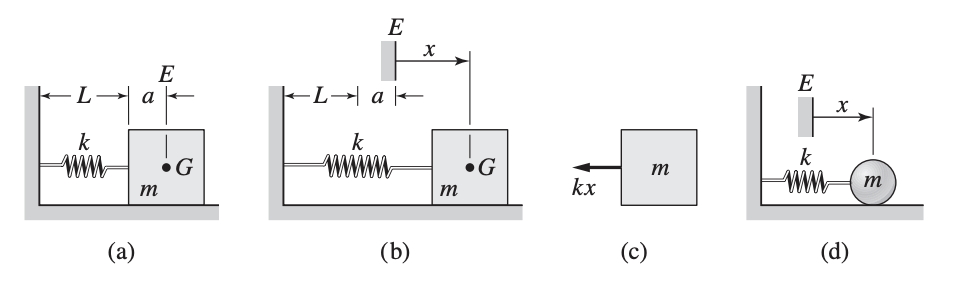
Newton’s 2nd law in combination with Hooke’s Law:
The mass is at equilibrium when the spring is at its free length ().
Equilibrium as Coordinate Reference
If we write the equation of motion based on the equilibrium position as the coordinate reference, the equation of spring systems will be .
Inclined Plane Example
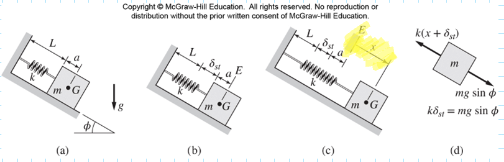
For a static deflection at equilibrium position, we would have:
In the above example, we have:
The term on the right side will be 0 at static equilibrium.
Vertical Spring Example
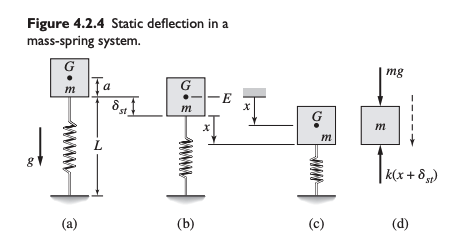
In the example above, we have:
where if the system is static.
Frequency
For a mass-spring system, the frequency of oscillation can be found as:
Solving for gives:
Converting to frequency form:
or