For a straight beam that is being acted upon by a positive bending moment in one axis:
- Top is in compression
- Bottom is in tension
- is neutral axis
- Not in tension or compression, strain is zero
- Coincides with centroidal axis
- is neutral plane – contains neutral axes for all cross-sections
Bending stress varies linearly with distance from neutral axis – further away from neutral axis means more stress. Graphically:
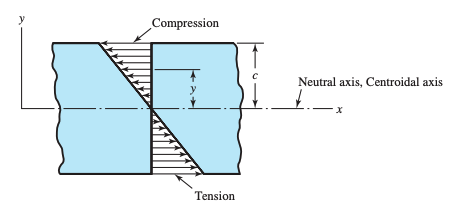
Mathematically, this is given by:
where is the distance from the neutral axis. Note that the negative sign makes it so that positive is compression, and negative is tension, just like we want.
- If the beam is bending downward, don’t use the negative!
is the moment of inertia or second moment of area about the -axis:
Obviously, the maximum magnitude of bending stress then occurs where has the greatest magnitude, such that:
where is the maximum magnitude of .
The above is sometimes written as:
where is called the section modulus. For rectangular beams, .
Bending due to Axial Loading
Normal stress can occur due to axial loading and loading, such that:
where is the bending moment.
is the axial loading, and it is:
- Positive if force is tensile
- Negative if force is compressive