A process is the change a system undergoes from one equilibrium state to another. Processes often involve either mechanical work or heat transfer.
Examples
For example, transferring a heated ball of iron to water would be a process involving heat transfer to water.
Another example is a truck with combusted diesel exhaust cooling down to normal temperature and pressure.
- Initial state: () – 2 independent, intensive properties as per the State Postulate
- Final state: () – state is specified (could calculate or other properties)
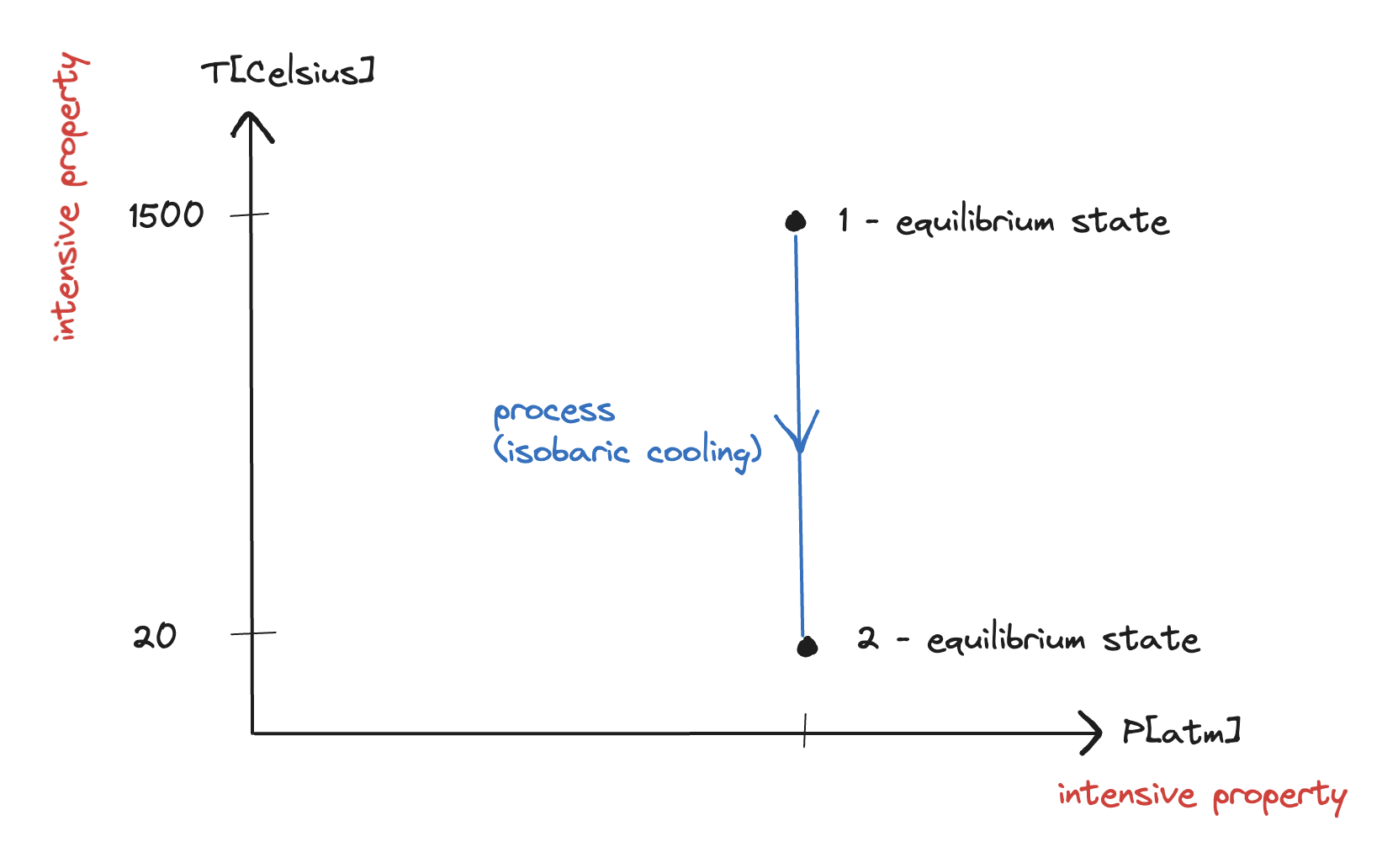
This is an example of an isobaric process.
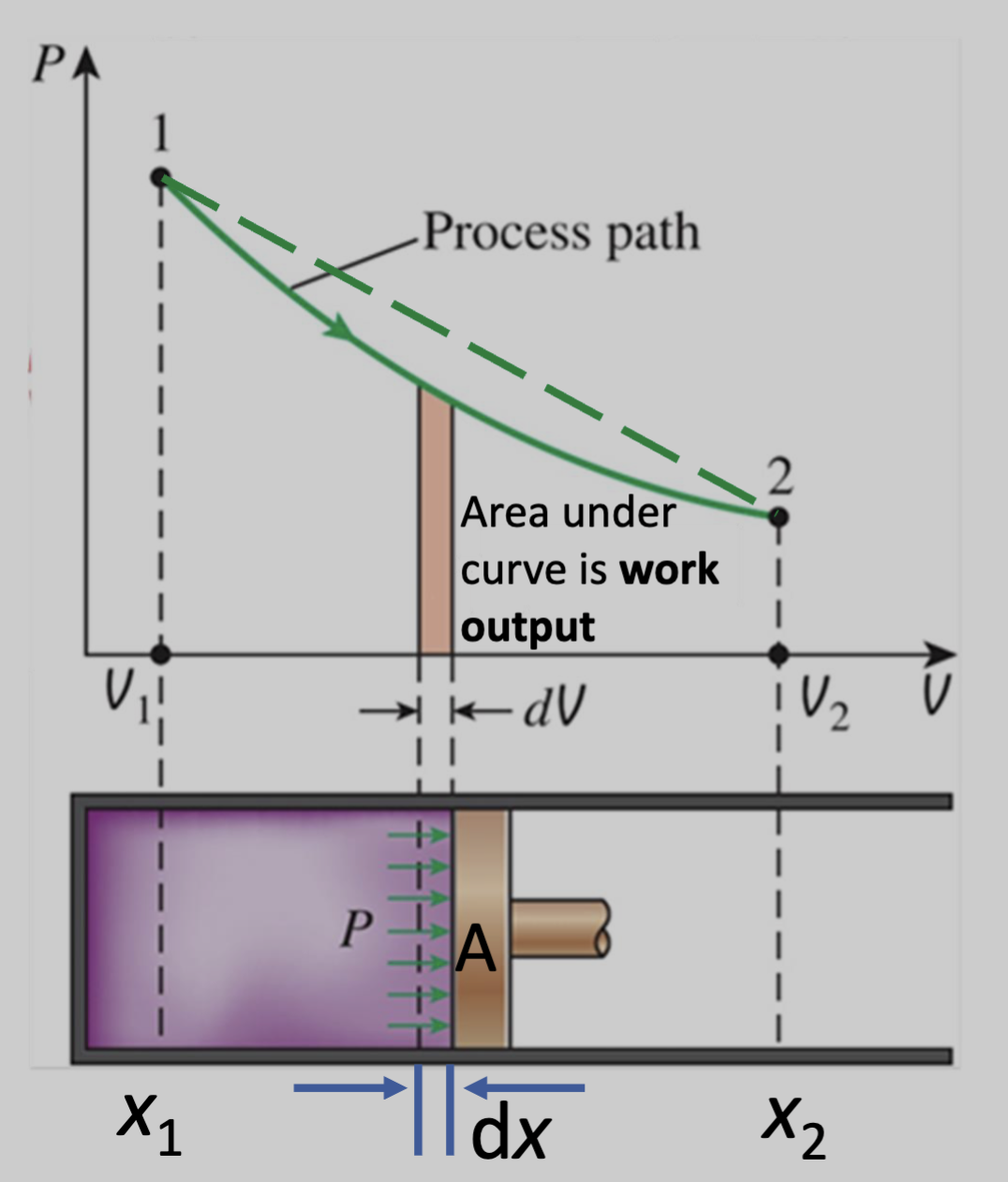
We can draw a state diagram like this:
Types of Processes
- Isobaric – constant pressure,
- Isothermal – constant temperature,
- Isochoric – constant specific volume,
- Adiabatic – no heat transfer
Work Done
Given a process path, the area under the curve is the work output.