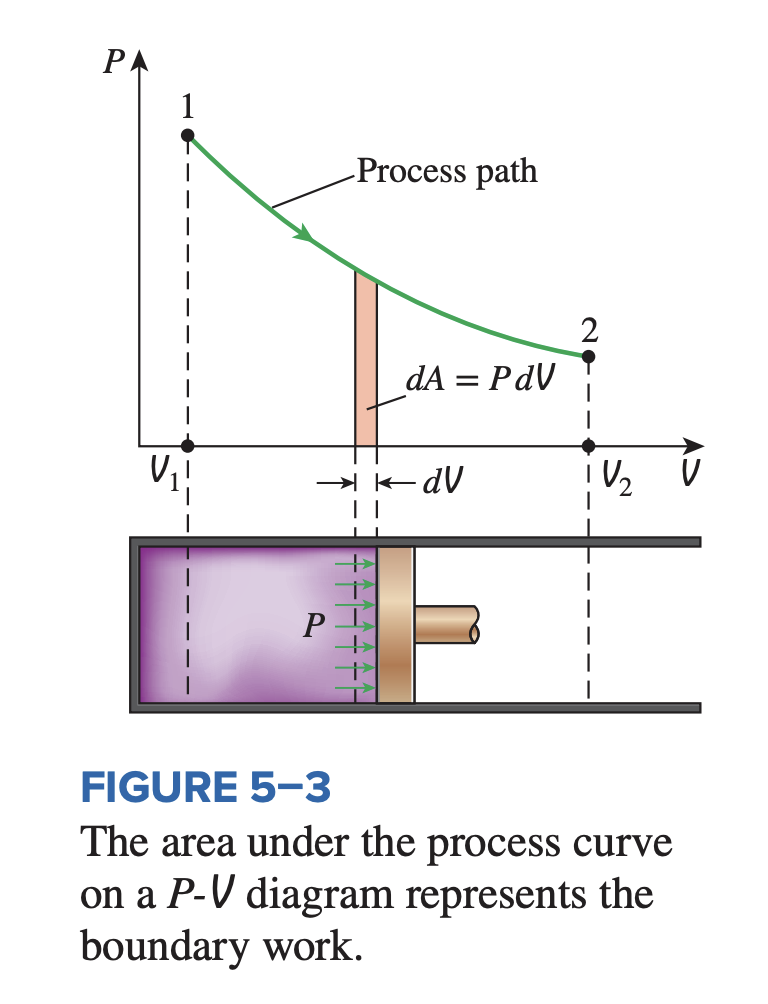
Moving boundary work is a form of mechanical work associated with the compression and expansion of a gas in a piston-cylinder device. During this process, part of the system boundary (the inner face of the piston) moves back and forth; therefore, this is called moving boundary work.
Work done by compression/expansion is given by:
- is the force, since pressure is defined to be .
Alternatively, we can use:
where means that pressure is a function of volume.
In general, the amount of work depends on the process path. This is also known as P-V work or boundary work.
Cyclical Boundary Work
Work is a path function – it depends on the path followed as well as the end states. If work were not a path function, no cyclic devices (car engines, power plants) could operate as work-producing devices. The work produced by these devices during one part of the cycle would have to be consumed during another part, and there would be no net work output.
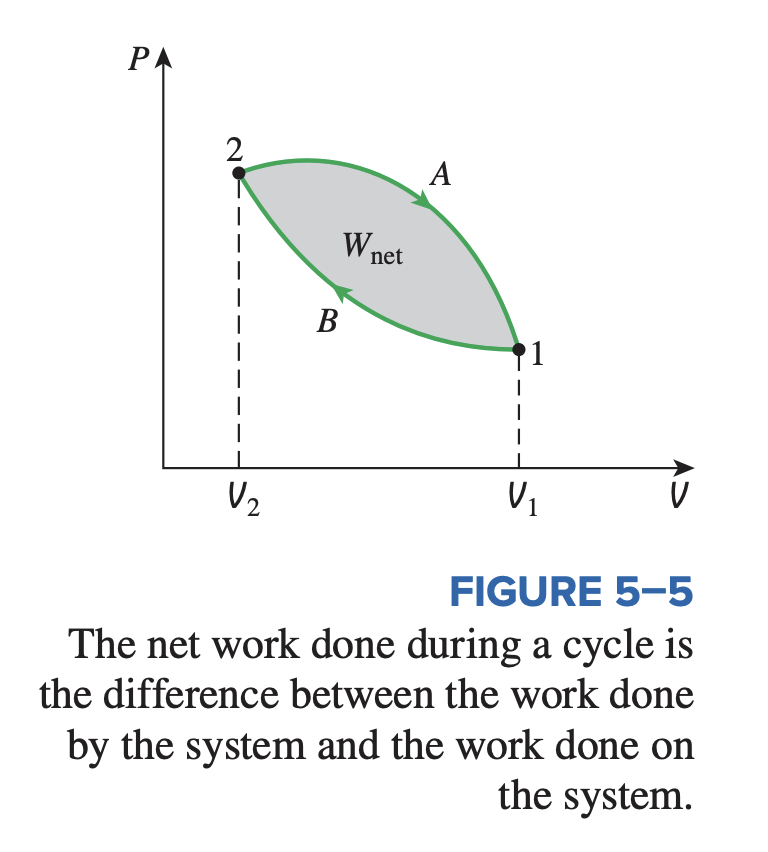
- In the above figure, net work is produced because the work done by the system to during expansion (area under path ) is greater than the work done to the system during compression