The general procedure is for diode circuit analysis is:
- Draw with diode off (removed from circuit). Solve for and any other unknowns like and .
- Draw with diode on (replace with source). Solve for and any other unknowns, like and .
- Use “off” model when and “on” when
Example
Use a basic diode model that does not conduct any current until 0.7V is applied, at which point it conducts any amount of current. Solve for and .
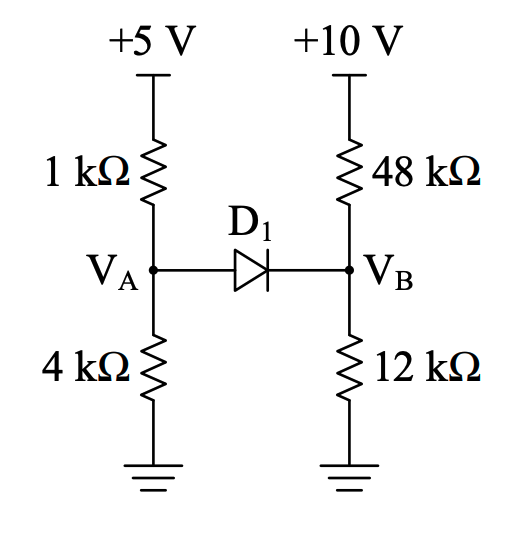
Step 1: Off model
First, we model the circuit with the diode off. Since the diode is off, we can basically just draw it as an open circuit:
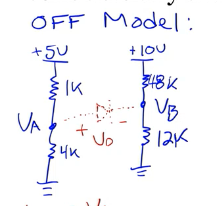
What’s the diode voltage when it’s off? We simply have:
Solving for and (as voltage dividers):
In the off-state, our diode voltage is .
Since and and don’t change in the problem, we know that the diode is on!
Step 2: On model
Now, we model the circuit with the diode on:
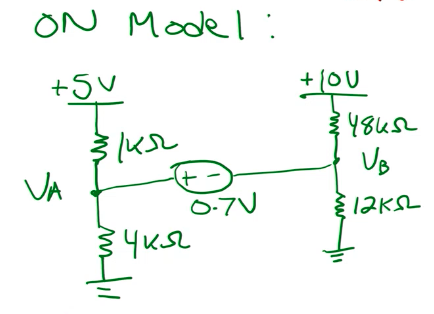
We can solve this using Supernodes:
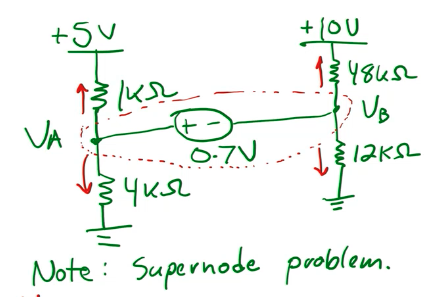
The equations are:
and
Solving this gives: