A diode is 2-terminal pn-junction device.
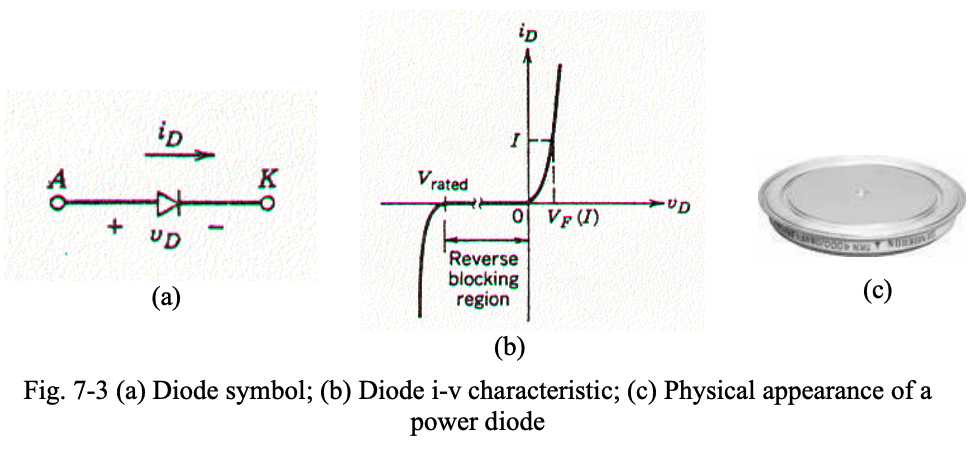
The diode conducts when it is forward biased (refers to the condition in which a diode or a similar component allows current to flow through it). This occurs when exceeds a threshold value, , called the forward voltage drop.
When reverse biased, the diode conducts a very small leakage current in the reverse direction. If the reverse bias voltage exceeds the reverse breakdown voltage, the device breaks down, resulting in dangerously high reverse currents.
A diode is an uncontrolled device; its on and off states are governed by the power circuit, not by a control signal.
Some useful MTE 220 notes: