A 2-wheeled robot typically has the following form:
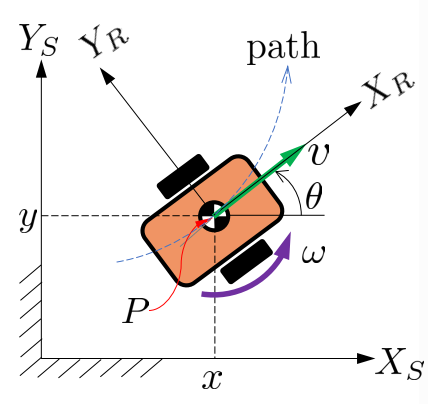
- Center of wheels
The forward velocity is tangent to the path:
Or:
- Usually, are treated as “inputs” and are treated as “state variables”
- The above constraint is an example of so non-holonomic constraints
Kinematics for wheel control
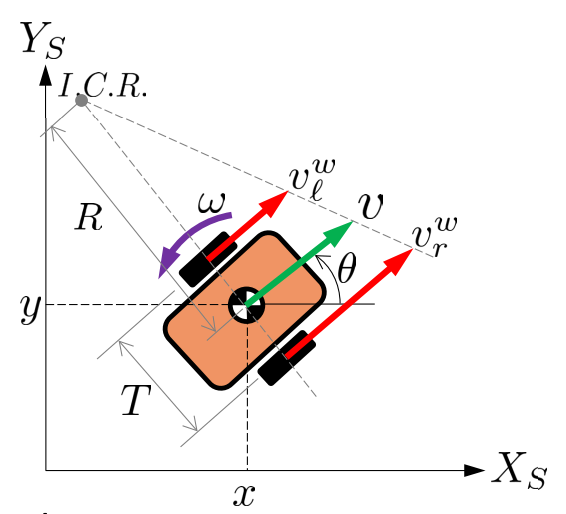
What are the wheel speeds to move the robot’s center point with and ?
- is the instantaneous center of velocity
- is the track width
- are the tangential linear speeds at the wheel rims (ground speed at contact points with no slip)
- In a left turn (), the right wheel traces a large arc and must spin faster and vice versa
Converting to wheel angular speeds:
- is the wheel radius
Working backward, we can then find and based on our wheel speeds:
and in turn: