A motion model is a mathematical description of how a robot’s inputs (like wheel speeds or motor commands) translate into changes in its state (position and orientation) over time.
Given coordinate frames:
- Reference frame; with axes
- Moving frame; with axes
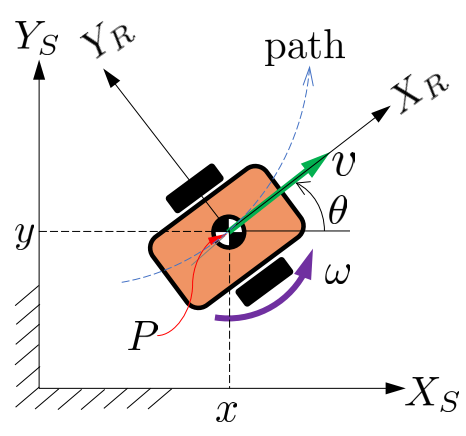
Main variables
Velocity variables (for a point in the body):
- – translational/linear velocity
- – rotation/angular velocity
Position variables:
- – horizontal position
- – vertical position
- – rotation angle
Different types of robot model describe relations between these variables.