Image processing is the set of operations applied to images (or video frames) to extract useful information or modify the image.

The key difference between image data and regular time-series is that images have a spatial (2D) distribution. Each pixel has two coordinates or . As such, operations that modify images must consider the spatial arrangement of pixels; image filters are 2D filters.
Spatial Filtering
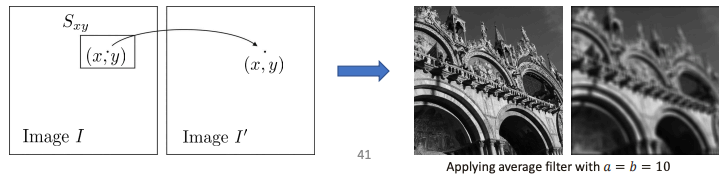
Spatial filtering (see Image Filter) is a fundamental operation in image processing, with the other being frequency domain filtering. A filter modifies each pixel based on its neighborhood; typically a small region around the pixel. Spatial filters are also called masks, kernels and windows.
A spatial filter has two main ingredients:
- A neighborhood of the pixel of the pixel under examination
- A predefined operation that is performed on the neighborhood
A typical spatial filter would look something like
where is a filter weight, are offsets from the pixel location, and define the neighborhood size.