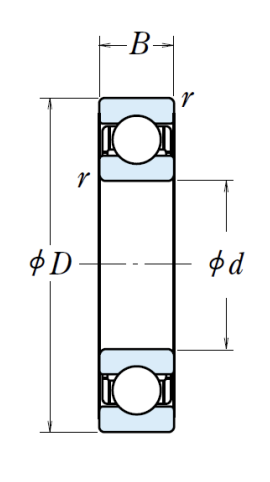
How do we select rolling element bearings? Specifically, we want to ==determine the outer diameter and width ==, given:
- Bore diameter, (shaft size)
- Applied load (radial, axial)
- Desired reliability
- Bearing life (in the unit of million revolutions)
Load Rating
Each bearing comes with a basic load rating:
- Static load rating or (radial direction). This is the load at which permanent static deformation will occur in the raceway and rolling element.
- is the equivalent static load, which is the actual applied load (or a calculated equivalent load) that the component experiences under static conditions.
- Static safety factor is given as
- Dynamic load rating (or to note radial direction)
- The (hypothetical) load that will give a life of 1 million revolutions. It is used to compute the (surface) fatigue life.
Bearing Life
Typically, the bearing life is denoted by where the subscript denotes the failure rate (in %).
- For example, life is the life of a bearing that 90% of the batch is survive under the design load (design load is specified in million rev’s)
- would mean that, out of 100 bearings manufactured as a batch, at least 90 of them will survive after 500 million revolutions of operations. Less than or equal to 10 are expected to fail.
The bearing life may also be given by hours of operation. This is usually the case for constant speed operations. Vehicle wheel bearings may also be specified in terms of mileage.
Given a speed in rpm, the hourly life is
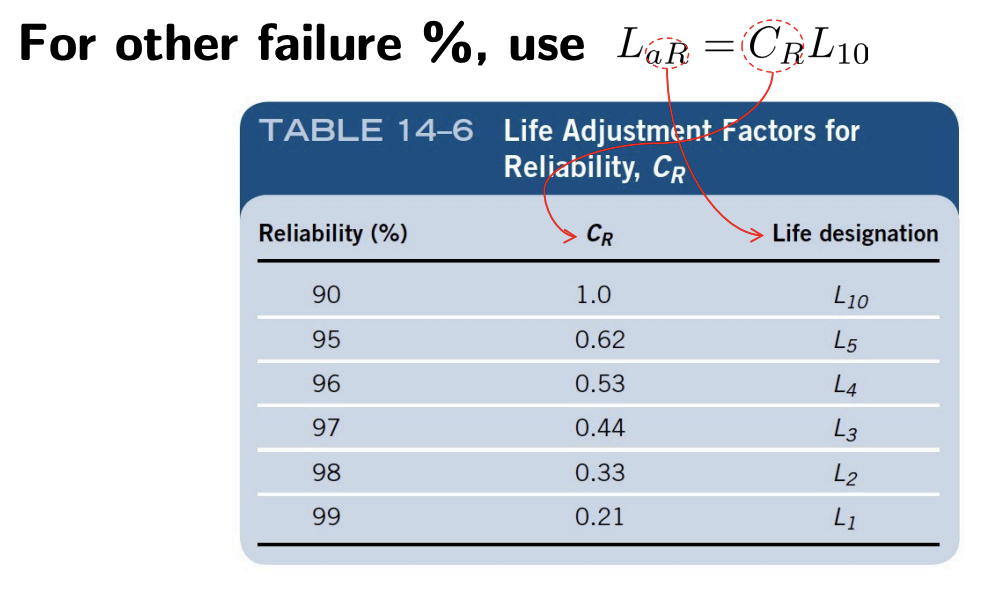
Bearings are typically rated based on . For other failure percentages (not 10%), use .
Bearing Life Equation (ISO281)
- Ball bearings:
- Roller bearings
where is the equivalent dynamic load.