A fluid is defined as a substance that that deforms continuously when acted on by a shearing stress of any magnitude.
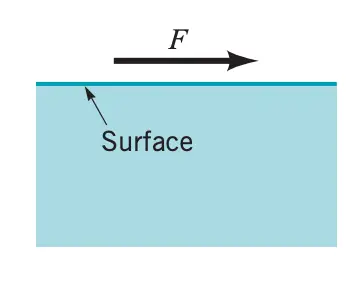
- When solids (steel or other metals) are acted on by a shearing stress, they will initially deform, but they will not continuously deform (flow).
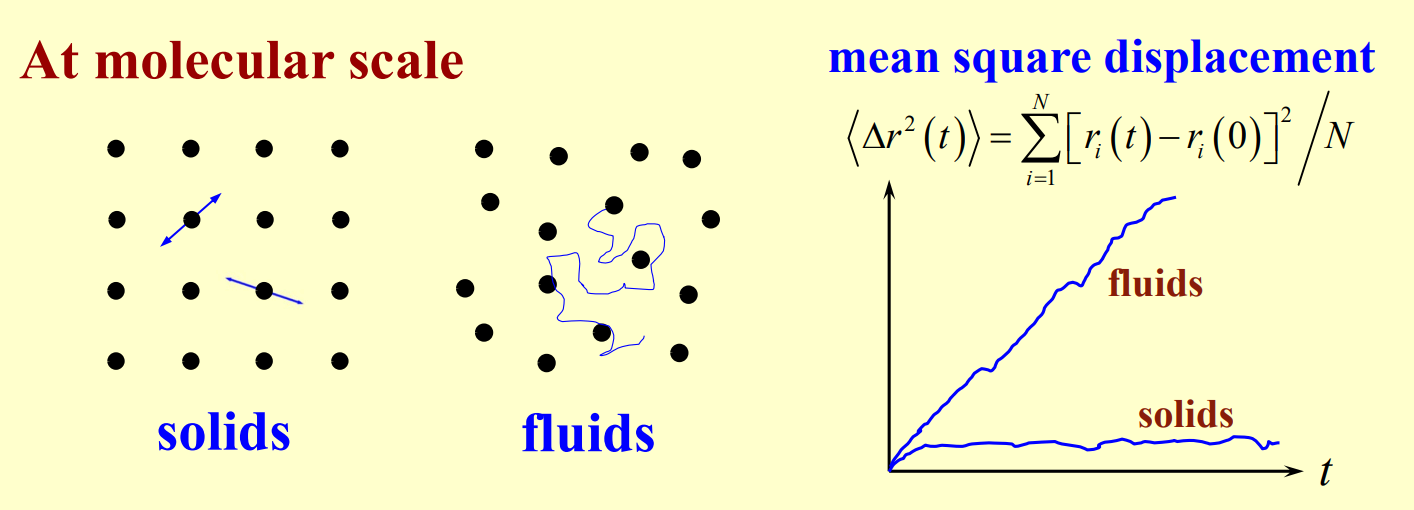
- Molecules in the solid are arranged in a fixed, orderly structure. They exhibit small vibrations but do not move freely
- Molecules are more randomly arranged and can move freely. Their paths are represented by squiggly blue lines, indicating diffusion-like motion.
- Mean square distance for fluids increases over time, while mean square displacement for solids stays mostly constant