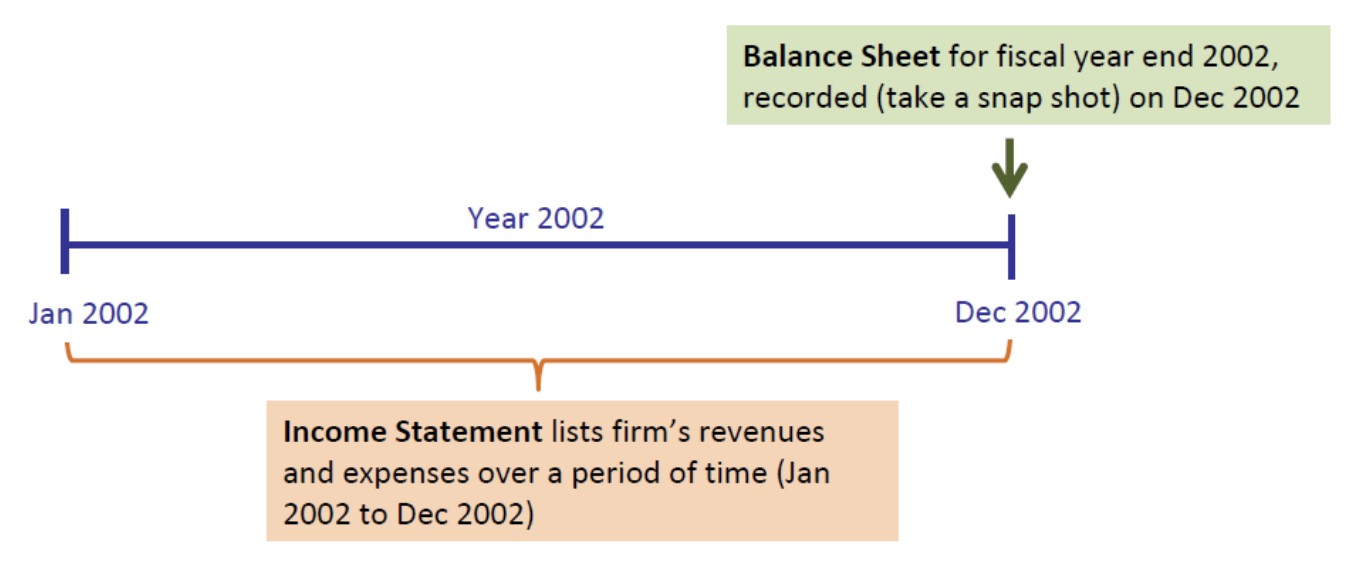
The income statement lists a firm’s revenues and expenses over a period of time. The bottom line of the income statement shows the firm’s net income, which measure its profitability during the period. Also called a profit and loss or P&L statement.
Earnings calculations include:
- Gross profit = Revenues (net sales) - Cost of sales
- Operating Income = Gross profit - Operating expenses
- Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) = Operating income Other income
- Pretax Income = EBIT Interest Income (Expense)
- Net Income = Pretax Income - Taxes
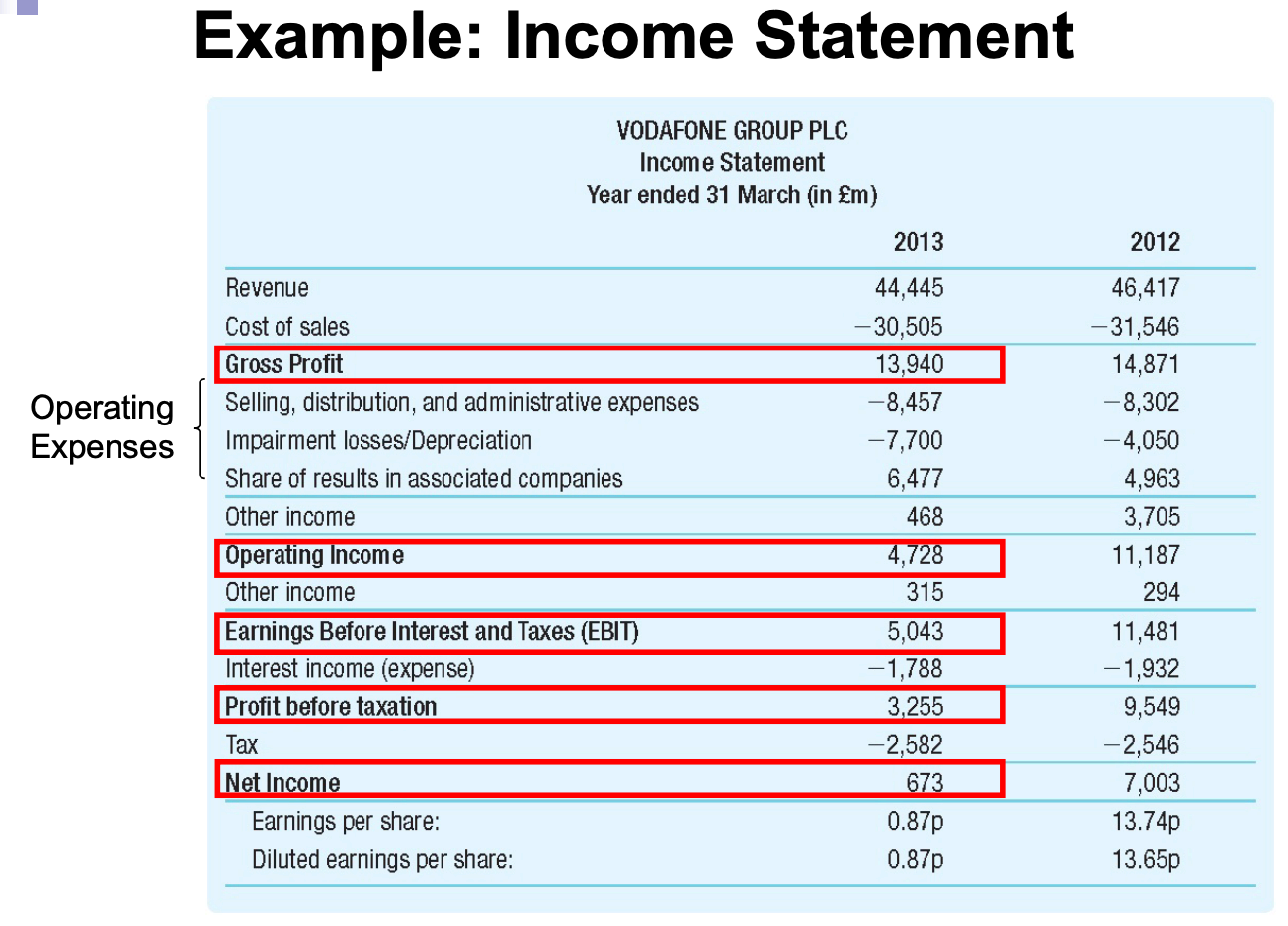
After net income, we also include earning per share:
- Earnings per share (EPS) = Net Income / Shares Outstanding
Note that EPS can be diluted because of large number of shares outstanding from stock options or convertible bonds.
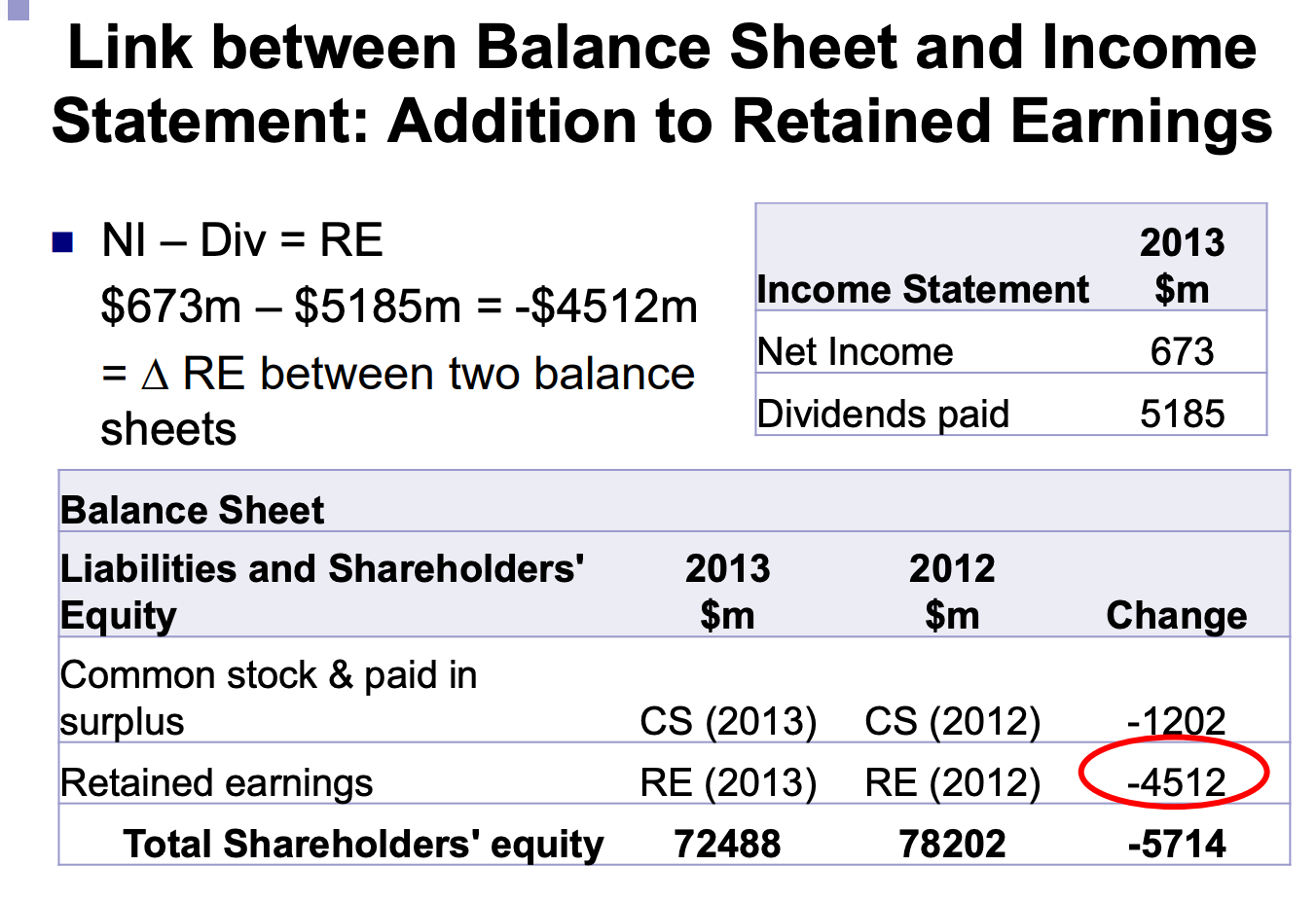
Net Income – Dividends is added to retained earnings.
Relation with Balance Sheet
The income statement shows the financial performance of the firm during the period leading up to the balance sheet date. The two statements are linked through the retained earnings account on the balance sheet, which shows the cumulative profits of the firm during its existence.