Structure
The balance sheet lists the firm’s assets and liabilities on the left and right sides:
- Left side:
- Current assets: Cash and other marketable securities
- Short-term, low-risk investments
- Easily sold and converted to cash
- Accounts receivable: Amounts owed to the firm by customers who have purchased on credit
- Inventories: Raw materials, work-in-progress and finished goods
- Other current assets: catch-all that includes items such as prepaid expenses
- Long-term assets: Assets that produce tangible benefits for more than one year
- Recorded value reduced through a yearly deduction called depreciation according to a schedule that depends on an asset’s life span. Depreciation is not an actual cash expense, but a way of recognizing that fixed assets wear out and become less valuable as they get older
- The book value of an asset is its acquisition cost less its accumulated depreciation
- Other long-term assets can include such items as property not used in business operations, start-up costs in connection with a new business, trademarks and patents, and property held for sale
- Current assets: Cash and other marketable securities
- Right side:
- Current liabilities:
- Accounts payable: The amounts owed to supplier’s purchases made on credit
- Notes payable and short-term debt: Loans that must be repaid in the next year, or repayment of long-term debt that will occur within the next year
- Accrual items: Items such as salary or taxes that are owed but have not yet been paid, and deferred or unearned revenue
- Long-term liabilities:
- Long-term debt: A loan or debt obligation maturing in more than a year
- Long-term debt: Book value of equity, net worth from an accounting perspective
- Current liabilities:
The balance sheet identity states that the left and right sides must balance such that
Purpose
The balance sheet shows the financial position of the firm at a specific point in time.
- a snapshot of the firm’s assets and liabilities e.g., values as of Mar 31, 2015
- amounts measured at historical values and historical exchange rates
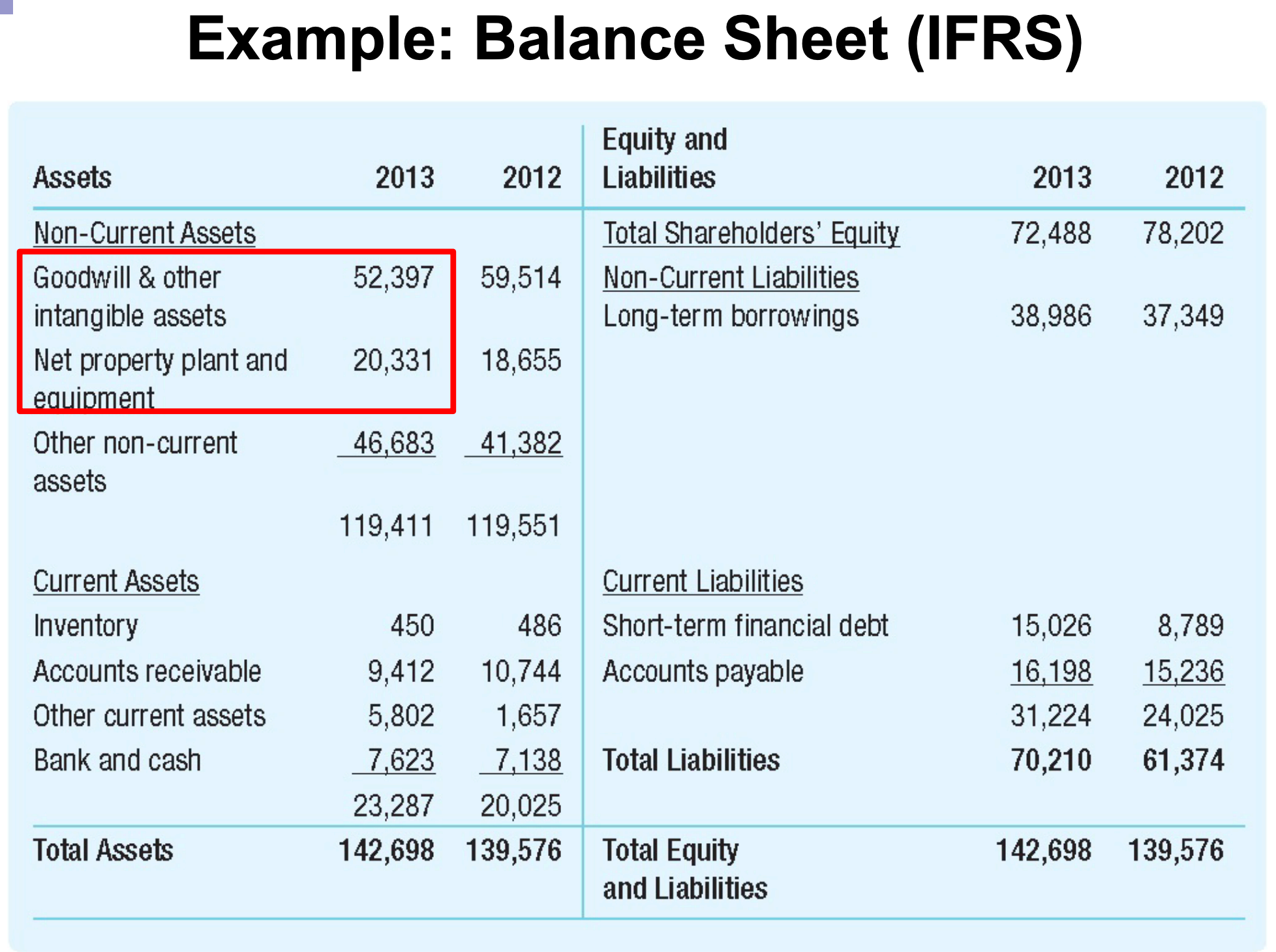
- Net Property, Plant, & Equipment
- = Acquisition cost – Accumulated depreciation
- = book value (carrying amount) of long-term assets
- Goodwill
- Acquisition price paid for a company above its book value
- Value of intangibles acquired by the firm