- Resolution: how finely a sensor can perceive changes, spatially (e.g. for a camera, resolution is the number of pixels) or in the sensing domain (e.g. the minimum difference in temperature detectable)
- Bandwidth/frequency: temporal resolution or the speed with which a sensor can provide a stream of readings, e.g. 30 fps of cameras
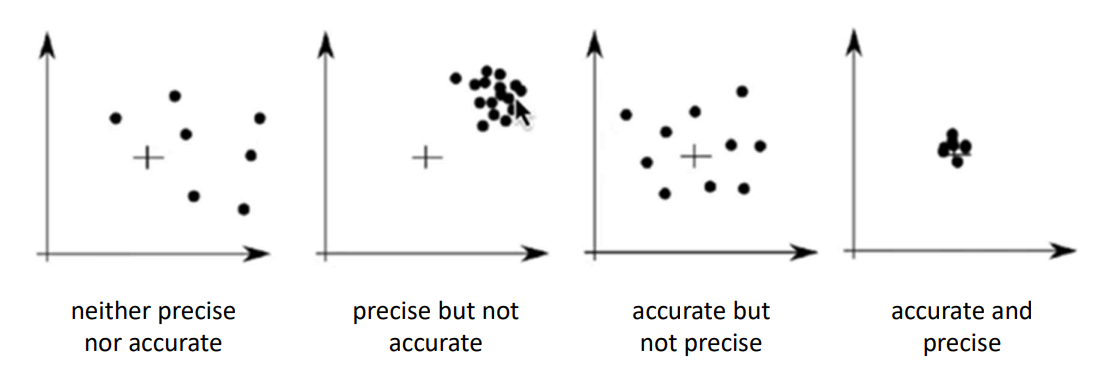
- Accuracy: the fidelity of a sensor to actually report the true value of the sensed quantity
- Precision/repeatability: the ability to predictably return the same measurement in the same physical situation; a sensor with good repeatability can be calibrated to improve its accuracy
- Aliasing: the behavior where the sensor can report the same measurement for more than one physical situation; for example, an IR sensor reports low values both for very near and very far objects