We can model an armature-controlled direct current (DC) motor with a load.
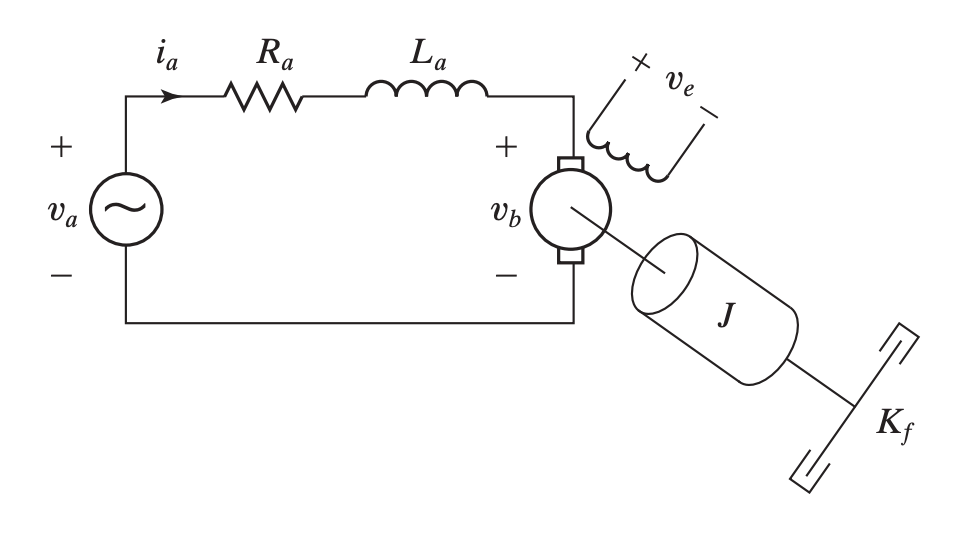
- Input: Armature voltage
- Output: Angular position of the motor shaft for position control, or angular velocity of the motor shaft for speed control.
- Intermediate variables: Armature current , angular position or angular velocity
KVL applied to the armature circuit gives:
Rotational version of Newton’s second law applied to motor shaft:
Position Control Case
We choose the state variables, input and output variables
State-space model:
and
Speed Control Case
If we replace with , we get the differential equation of a DC motor system in the speed control case:
State-space model:
and