Wheels are common examples of systems undergoing general plane motion with both translation and rotation.
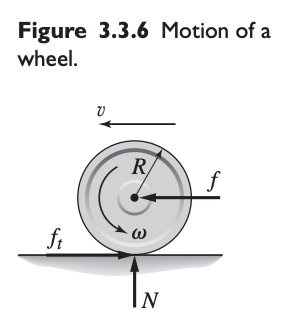
The wheel shown below can have 1 of 3 possible motion types:
- Pure rolling motion. This occurs when there is no slip between the wheel and the surface. IN this case, .
- Pure sliding motion. This occurs when the wheel is prevented from rotating (such as when a brake is applied). In this case, and .
- Sliding and rolling motion. In this case . Because slipping occurs in this case, .
The wheel will roll without slipping (pure rolling) if the tangential force is smaller than the static friction force , where is the force of the wheel normal to the surface. In this case, the tangential force does no work because it does not act through a distance. If the static friction force is smaller than , the wheel will slip.