Block diagrams consist of four basic symbols:
- Arrow – Used to represent a variable and the direction of the cause-and-effect relation
- Circle – Represents addition as well as subtraction, depending on the sign associated with the variable’s arrow
- Block – Used to represent the input-output relation of a transfer function
- Take-off point – used to obtain the value of a variable from its arrow, for use in another part of the diagram

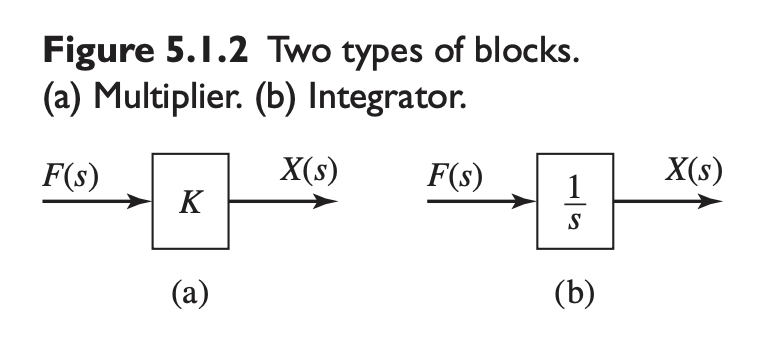
- (a)
- (b)
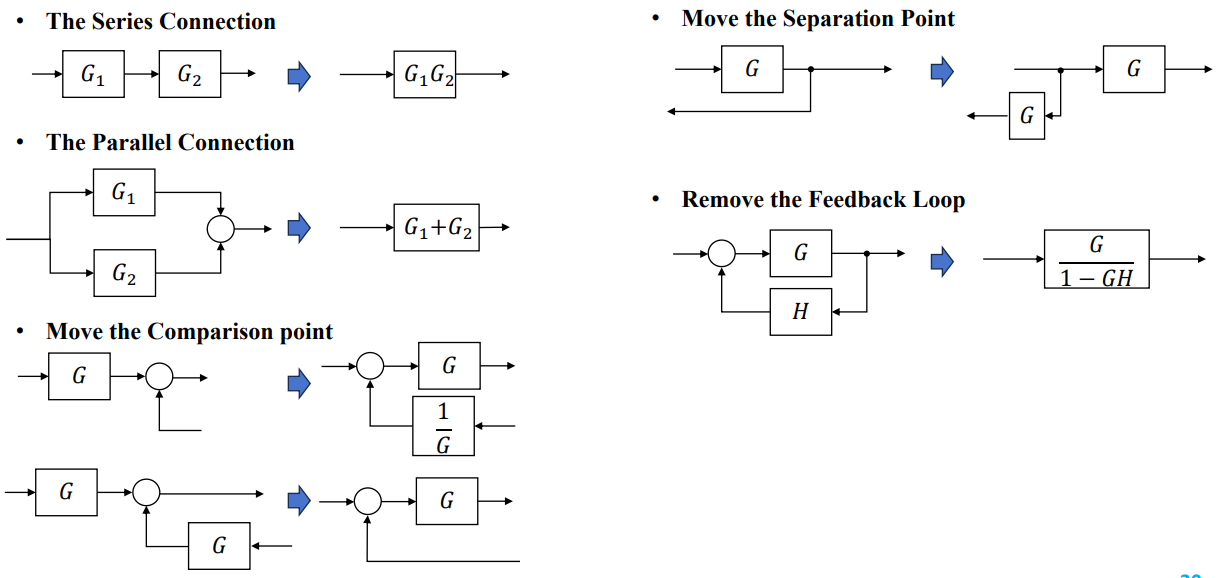
Equivalent Block Diagrams
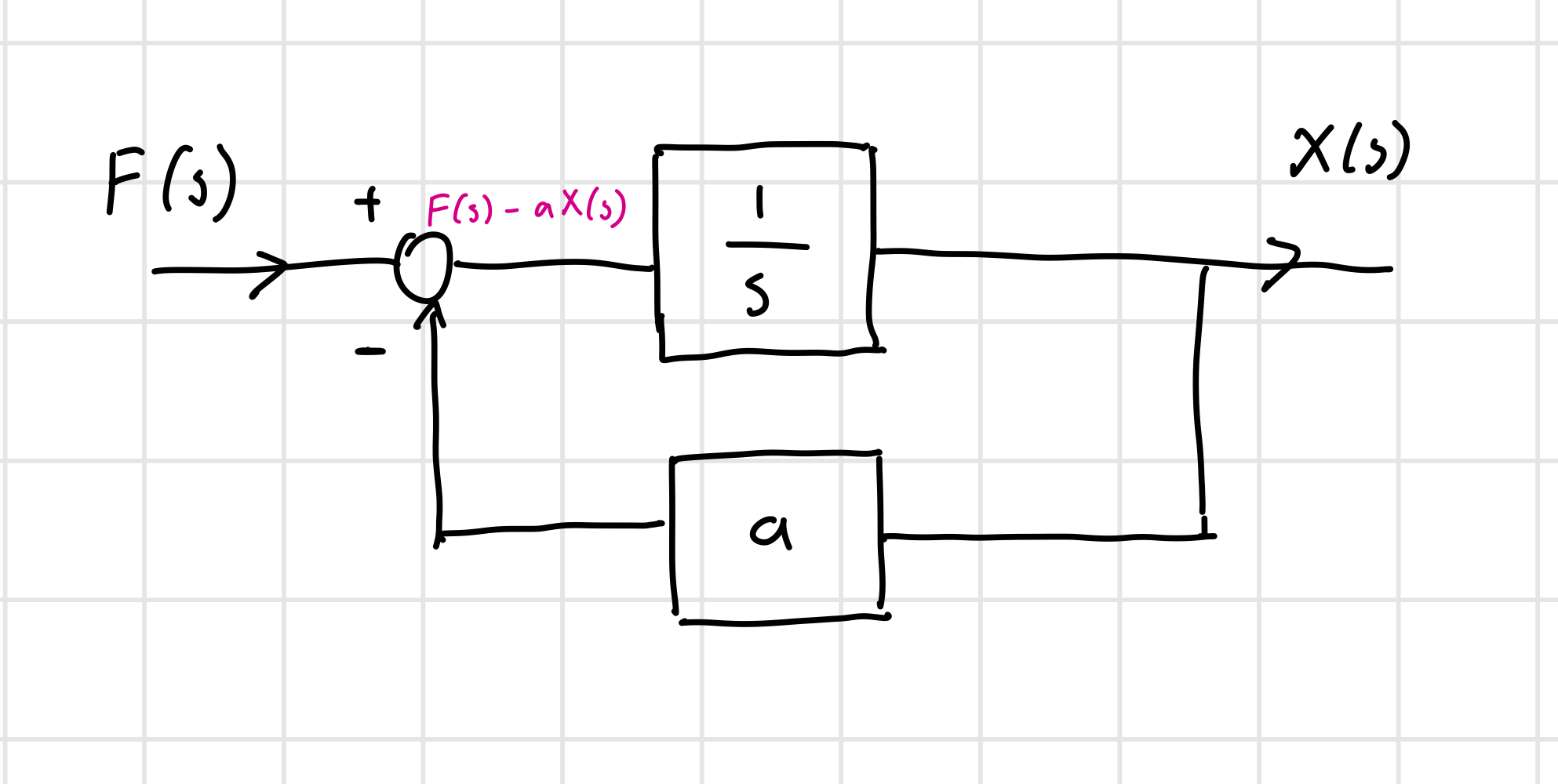
Let’s say we have a system described by:
In Laplace domain:
Then, our transfer function is:
or
In block diagram form:
Examples
- Example 1: Mass-spring system with Dampener
- Example 2: Simple feedback loop system
- Example 3: Numerically defined system
- Example 4: Complex multi-DOF mass-spring system