Let’s say we have a uniaxial stress in the -direction (the figure below is an uniaxial load).
- Under a direct axial tensile load, member will stretch and lengthen
- Under a direct axial compressive load, member will compress and shorten
This is often called pure tension or pure compression or “simple tension/compression” to indicate there are no other effects. Some assumptions:
- Bar is straight and made of homogeneous material
- Line of action of force contains centroid
- Section is not taken at: the ends, a discontinuity, or abrupt change in cross section
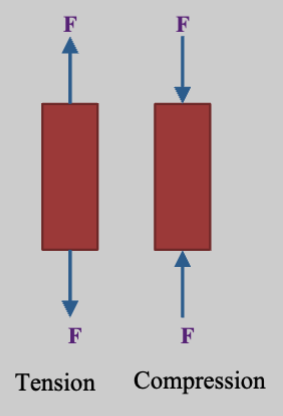
The normal stress is:
The strain is:
Stress and strain can be expressed with Hooke’s law:
where is the material-dependent Young’s Modulus (aka modulus of elasticity).
The displacement can be written as:
where is the cross-sectional area.