A controllable switch can be turned on and off by a control signal.
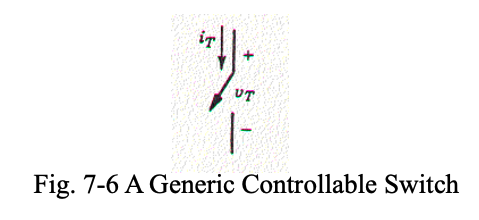
When forward biased, the switch can be turned on by applying a positive voltage or current at the control terminal (gate or base).
When in the on state, the switch can be turned off by applying a negative voltage or current at the control terminal (gate or base).
When on, the switch conducts current in one direction only (except for MOSFET).
When off, the switch blocks may only block positive voltages, or both positive and negative voltages, depending on the switch type.
Types of controllable switches:
- Bipolar Junction Transistor (BJT)
- Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET)
- Gate-Turn-Off Thyristor (GTO)
- Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor (IGBT)
- Integrated Gate Commutated Thyristor (IGCT)
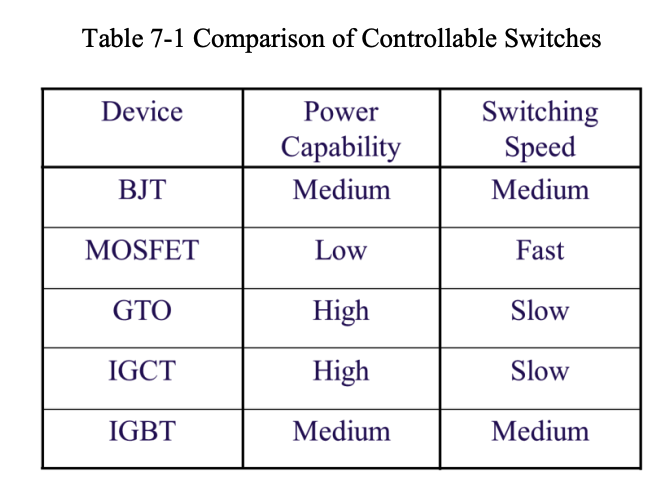
Table 7-1 compares the controllable switches in terms of power capability (rated voltage and current) and switching speed (switching frequency).