A Zener diode relies on the reverse breakdown voltage. is generally poorly controlled, while can be well-controlled.
Zener diodes operate right on the edge of breakdown to provide a reasonably precise voltage.
- Given a specific , a Zener diode will drop across it
- Choose a precision resistor, , to drop the rest of the voltage This has much better voltage regulation than a resistor voltage divider. Use this when we need good voltage regulation but not a complete voltage supply!
Analyze just like a regular diode, using instead of .
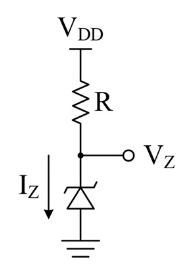
Example
Problem: Say that , and the datasheet says to use . Choose to drop excess voltage. Assume is a supply.
The Zener diode is going to lock in at 3 volts, so the voltage across our resistor is the leftover 2 volts. Knowing that , we have:
Extra: we can find the static (“all the time”) power of the diode: