Mesh analysis refers to the application of KVL to solve a circuit by finding all the mesh currents, which is a component of the actual current you would measure through a wire in a circuit.
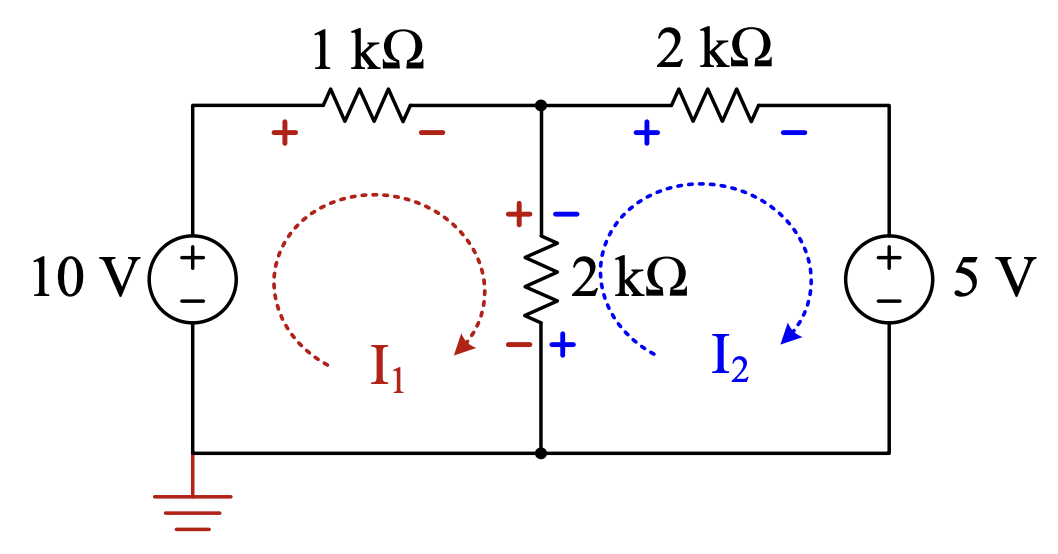
- would be measured flowing out of the source and through the resistor.
- would be measured out of the top resistor and into the source.
- The middle resistor experiences the summation of these two independent mesh currents as flowing into the top terminal or flowing into the bottom terminal.
Mesh Analysis steps:
- Label mesh currents and ground.
- Write the KVL equations around each mesh, referencing mesh currents under consideration as entering the positive terminal of components where no polarity is specified. For example, voltage sources have polarity but resistors do not.
- Replace currents with device equations using the node voltages:
- Solve .
Alternatively, you can just write the sign that the mesh current “runs into” as it progresses around the mesh. For example, runs into the negative terminal of the 10V source, so the sign of that term is negative:
This is mathematically equivalent (it’s just multiplying both sides by ). This simple change eliminates the need to consider whether a device adds or removes energy from the charge flowing through it, stepping the voltage up or down.