Batteries are electrochemical cells whose voltage are determined by chemistry, , not size (AAA vs. D). There are rechargeable and non-rechargeable ones.
- Non-Rechargeable (“Primary”):
- Typical alkaline battery
- Rechargeable (“Secondary”):
- Lithium-Ion (LiIon), Lithium Polymer (LiPo), Nickle Metal Hydride (NiMH), Nickle Cadmium (NiCd)
- Widely varying
A very basic model of a battery is to consider it as a voltage source. However, this is a vast oversimplification as there are lots of factors like internal resistance, aging, etc.
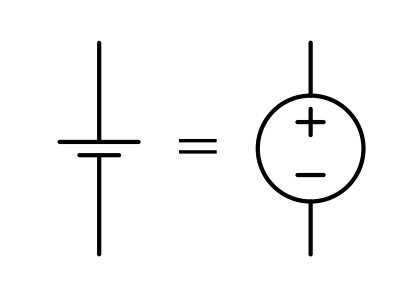
Battery Summary
- Batteries have very complex behaviour
- is chemistry dependent (SoC curve too)
- increases with physical size, proxy for
- (series)
- (parallel)
-
- E has units of joules () or watt-hours ()
- State of charge: SoC, like an indicator: 0 = Empty, 1 = full
- “Discharge curve” – plot of V vs SoC, depends on chemistry
- Recharge: , values depends on chemistry
