Definition
The Secant Method is conceptually similar to the Newton-Raphson Method but uses an approximation of the derivative (backward difference) in the equation:
This backward difference is a first-order/linear approximation of derivative using previous value:
Subbing this into the Newton-Raphson equation (1) gives:
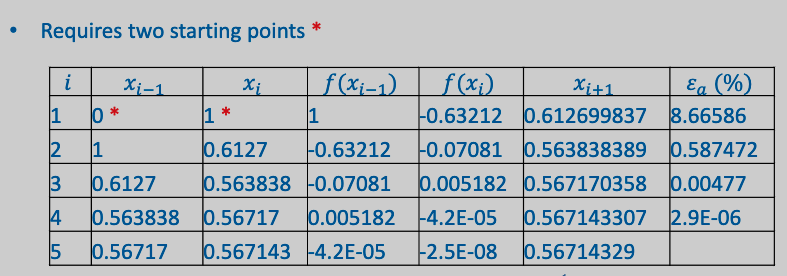
This also means that you require two starting points.
Notes
- Similar convergence properties to Newton-Raphson, but don’t have to .
- The fact that you don’t have to find the derivative means that this is good for functions that are complex and hard to differentiate.
Example
I was too lazy to write this one out lol.