- Taking variables, return a vector
- Vector functions of a single variable in and :
- where are “component functions”
- Domain = set of all ‘s for which the component functions are defined
Vector Function Domain Example
- : All ’s
- :
- :
- Graph of vectors – think of vector returned by the vector function as a position vector for points
- Position vector is a vector that starts at origin and goes to
- Basically just plug values in and plot points according to the resulting position vector
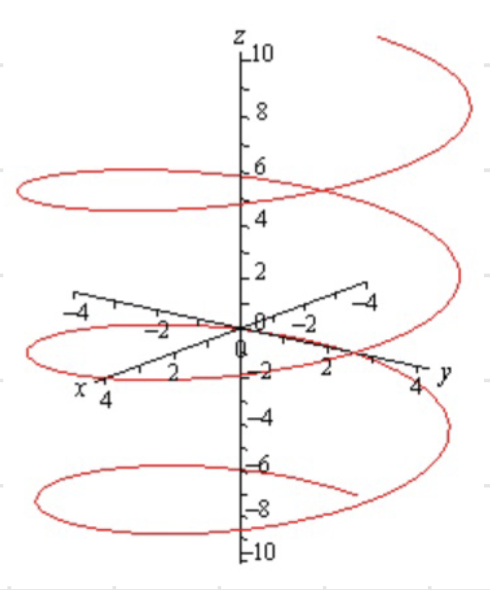
Vector Function Graphing Example
Since the -axis is not constant, we will get a spiral about the -axis Spiral revolves around axis with .
Determining the vector equation of a line segment
Let’s say we have a segment starting at and ending at . We can use these points as info. Find direction of the line with: Then, using direction and point , we then have:
Since we want the segment to start at and , we need to restrict :
- Notice that and
- Thus we can just restrict Then, we have:
2-variable Vector Functions
Graphs become surfaces.
2-variable Vector Function Example
Parametric form: Elliptic paraboloid (-axis)
Any 1-variable or 2-variable can be written in vector form:
1-variable:
2-variable:
Example: