Random Sample Consensus (RANSAC) is a basic tool in computer vision and feature extraction. In the most prototypical case, it is used to find a line of best fit. It’s particularly good for noisy data.
The basic idea of RANSAC:
- Randomly select two points from the data set and draw a line
- Construct an “inlier set” by collecting all points close to this line by some specified threshold distance
- Repeat the process until you get the inlier set with maximum data
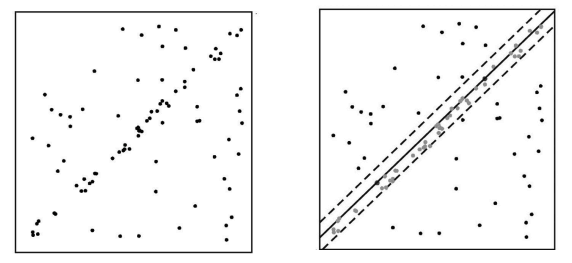
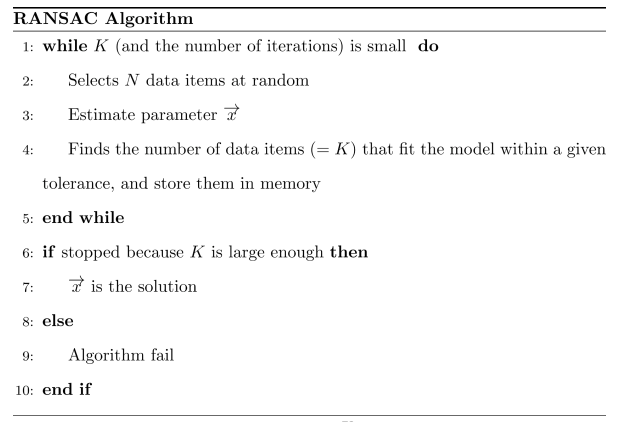
Pros:
- Robust to outliers and noise
- Can trade off accuracy for speed
- Very general concept that can be applied to a wide range of features
Cons:
- No upper bound on the time it takes to get the solution
- Does not guarantee the optimal solution (not even the existence of a solution)
- Can estimate only one entity (e.g. only one line)