The synchronous speed () of an induction motor refers to the speed at which the rotating magnetic field inside the motor operates. It is an ideal speed synchronized with the frequency of the AC power supply.
Configurations
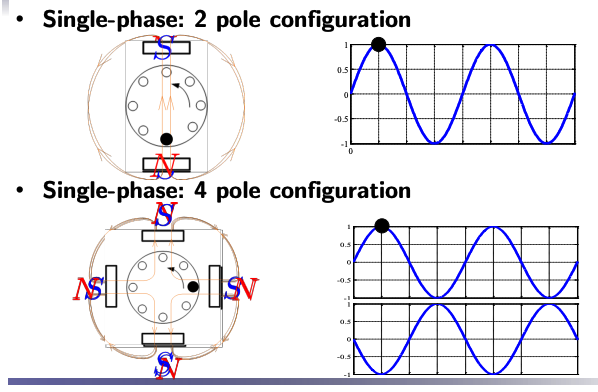
Single-Phase Induction Motor Configurations
- In the 2-pole configuration, the alternating magnetic field completes one full rotation for each AC cycle.
- In the 4-pole configuration, the alternating magnetic field completes only half a rotation for each AC cycle. It takes two cycles to complete one full rotation. This reduces the synchronous speed to half compared to the 2-pole configuration.
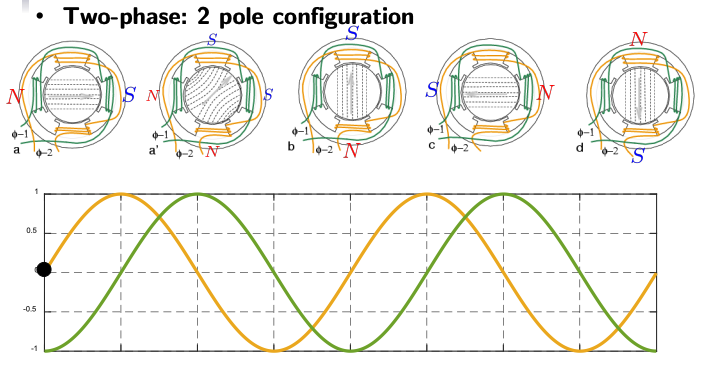
2-Phase Induction Motor Configurations
- The two-phase system involves two windings separated by 90 degrees, creating a more balanced rotating magnetic field.
- As shown in the figure, each winding generates a sinusoidal magnetic field, with a 90-degree phase shift between them, producing a smoother rotation.
- Similar to single-phase, in a 2-pole configuration, the magnetic field completes one rotation for each AC cycle.
Observations for Phase Configurations
- Single-Phase Motor:
- 2-Pole: 1 rotation for 1 AC cycle (2 pole faces).
- 4-Pole: 1/2 rotation for 1 AC cycle (4 pole faces).
- 2-Phase Motor:
- 2-Pole: 1 rotation for 1 AC cycle (4 pole faces).
- 4-Pole: 1/2 rotation for 1 AC cycle (8 pole faces).
- 3-Phase Motor:
- 2-Pole: 1 rotation for 1 AC cycle (6 pole faces).
- 4-Pole: 1/2 rotation for 1 AC cycle (12 pole faces).
Synchronous Speed Formula
The synchronous speed of an induction motor is given by
where is the AC power frequency in Hz and is the number of poles. The unit for is rpm.
Note that the pole number is independent of the number of phases:
- 2 pole 1- motor has 1 pair (or 2 pole shoes) of coils
- 2 pole 3- motor has 3 pair (or 6 pole shoes) of coils
Synchronous Speed Example
Synchronous Speed Example Question
- What is the synchronous speed of the shaded pole induction motor (120V 60Hz AC power)?
- For a 3-phase induction motor, the speed is observed to be around 870 rpm when the AC power runs off 60 Hz frequency. What is the pole number of this induction motor?
A shaded pole motor is essentially a 2-pole single phase motor with a self-starting mechanism. Thus, we have:
Usually they run rpm.
Note: Capacitor start induction motor also acts as a 2-phase. So, for a 2 pole motor, .
Slip and Induction Motor Speed
An induction motor can never reach the synchronous speed, because then there is no induction (and thus no torque produces).
The relationship between the actual speed of the motor and the synchronous speed is expressed by the slip ():
This can be re-arranged to express the actual speed of the motor:
Slip is typically as a percentage and indicates how much slower the rotor is moving compares to the rotating magnetic field. Actual speed is always less than , as some slip is essential for torque production. Higher torque demand causes an increase in slip.