A sudden expansion of flow in a pipe is a unique case where a theoretical result for energy result is available.
In a sudden expansion, fluid flows from a smaller cross-sectional area to a larger one . This expansion creates flow separation and turbulent mixing, leading to significant energy loss.
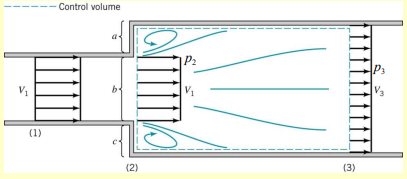
The analysis of a sudden expansion is based on three fundamental conservation principles:
- Mass conservation:
- Momentum conservation:
- Energy conservation:
From the momentum conservation expression, we can find the pressure difference as:
This indicates that the pressure after expansion () is lower due to the velocity difference created as fluid decelerates. The pressure recovery is incomplete because of energy dissipation through turbulence.
The head loss during a sudden expansion is derived from the energy conservation equation:
or, alternatively we can write
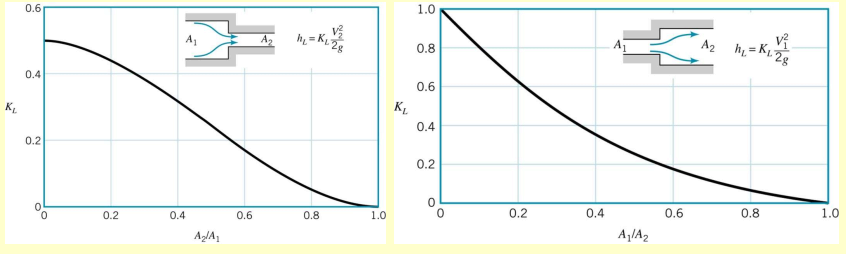
The loss coefficient for a sudden expansion is expressed purely in terms of velocity and area ratios: