In an amortizing loan:
- All payments are equal
- The loan is fully repaid with the final payment.
For example, a $30,000 loan paid over 60 months:
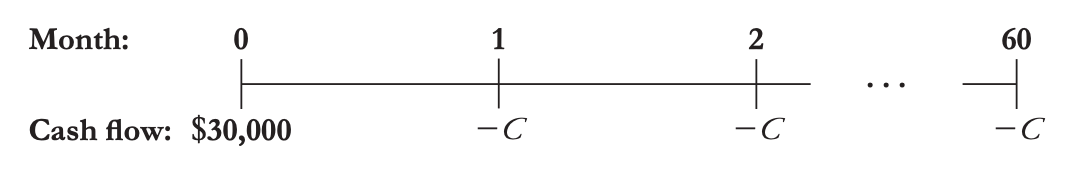
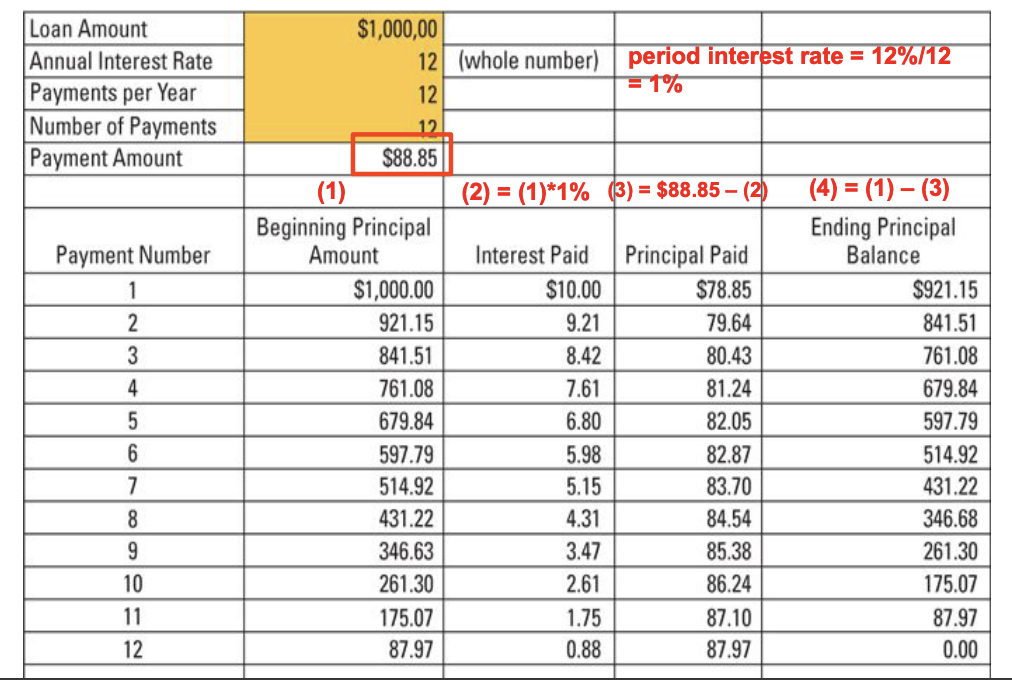
- Regular fixed amount of payments cover both repayment of principal and interest on remaining loan amount
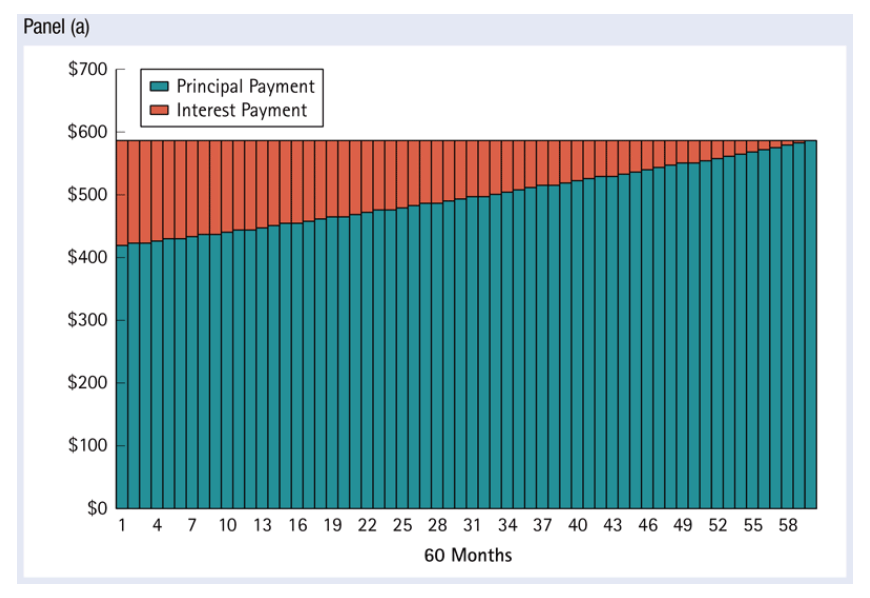
- Portion of principal repayment and interest from each payment is different throughout the term
- Portion of interest in the repayment is decreasing
- Portion of principal in the repayment is increasing
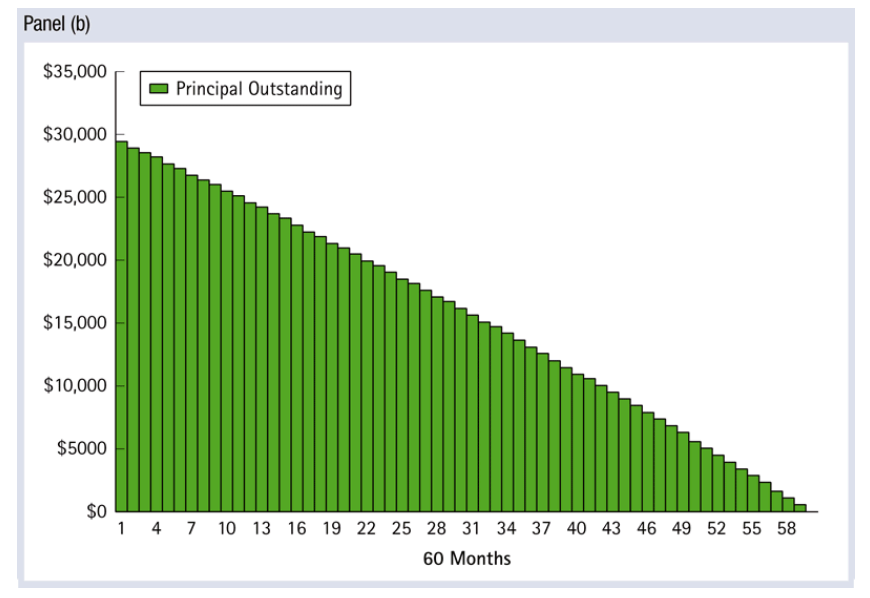
- Principal outstanding (balance) is declining
Payment Amount
We can find the payment amount by considering it as an annuity. Recall that annuities have present value:
Thus to find the payment amount, we have:
where is the original payment.
Outstanding Loan Balance
The outstanding balance on an amortizing loan is different each month. The amount owed can be calculated as the present of future obligations on the loan. So the outstanding balance (aka outstanding principal) is equal to the present value of the remaining future loan payments.