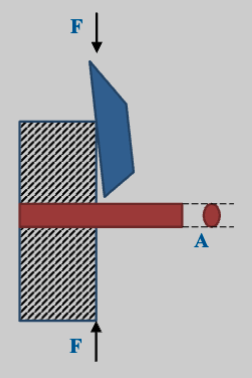
Direct shear stress occurs when an external force is applied parallel to the surface area of a material, causing one layer of the material to slide over an adjacent layer. Basically, there is shearing action with no bending. This type of stress is often encountered in scenarios where forces are trying to cut through a member.
- For example, scissors, shears, punch and die, or a key shearing off between a shaft and hub.
This direct shear stress can be written as:
where is force, is area in shear, and is shear stress.