Below we have the circuit symbol for an ideal transformer:
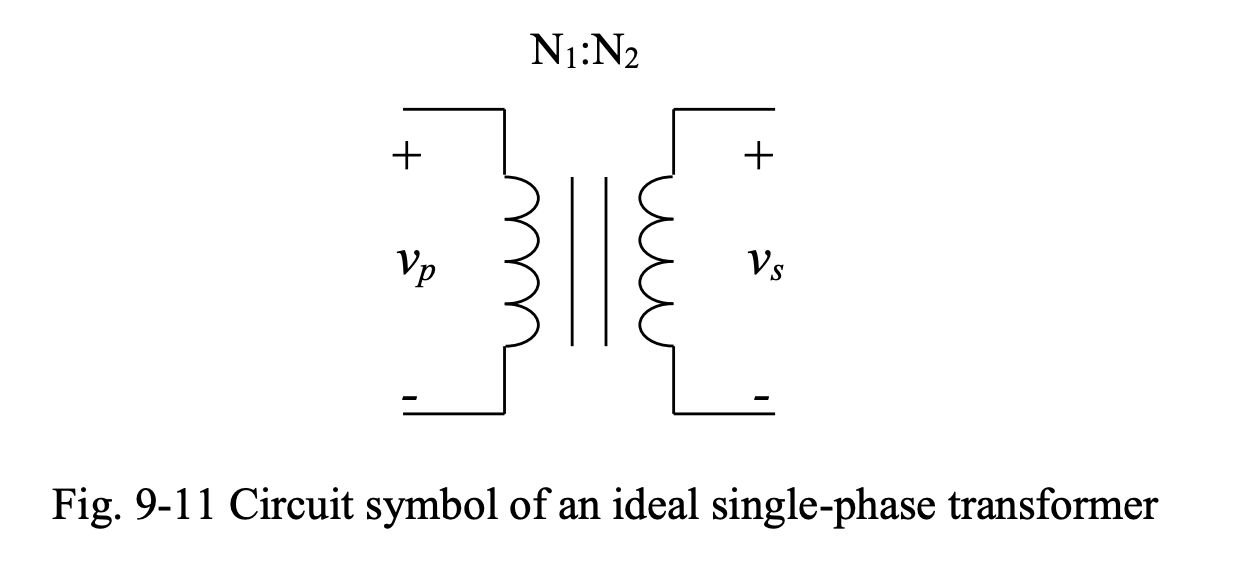
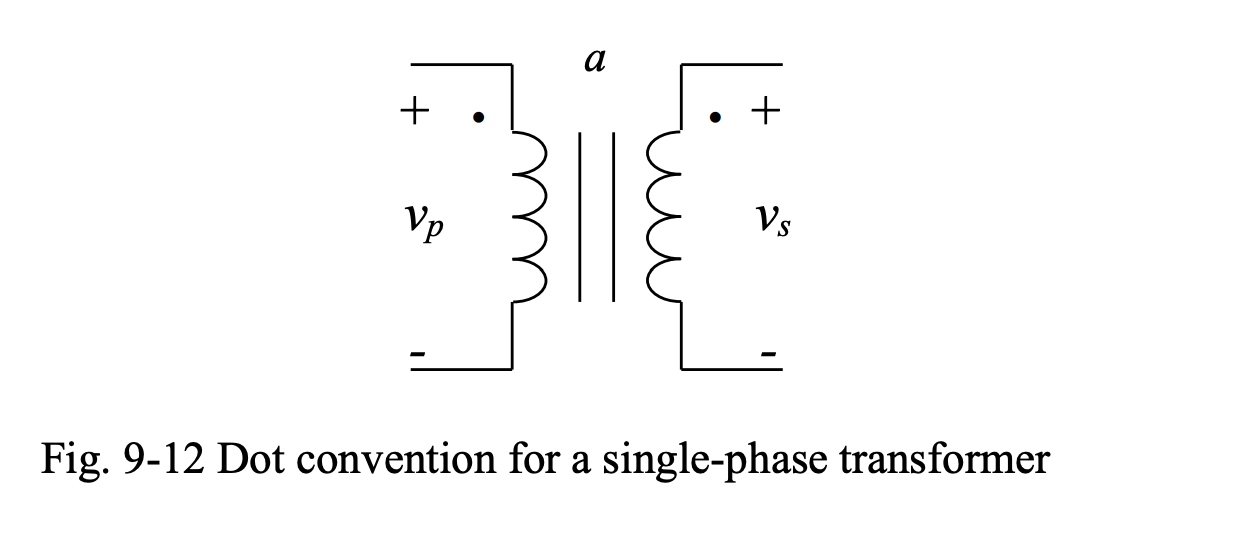
This circuit is missing an important piece of information; the relationship between the polarities of the voltages and the directions of the currents on two sides of the transformer based on the way the transformer’s primary and secondary windings are wound.
The dot convention conveys this information as follows:
- If the dotted terminal on the primary-side is at a higher potential with respect to the undotted terminal, then, the dotted terminal on the secondary-side will also be at a higher potential with respect to the undotted terminal.
- If the primary current enters the dotted terminal on the primary side, the secondary current leaves the dotted terminal on the secondary-side.