In a transformer, a large cross-sectional area is required to ensure a small reluctance, based on
This is for easy magnetic flux setup, and ensures that the flux density does not exceeded its maximum allowable value. As a result, the transformer will be operated in the - curve and the core is not saturated.
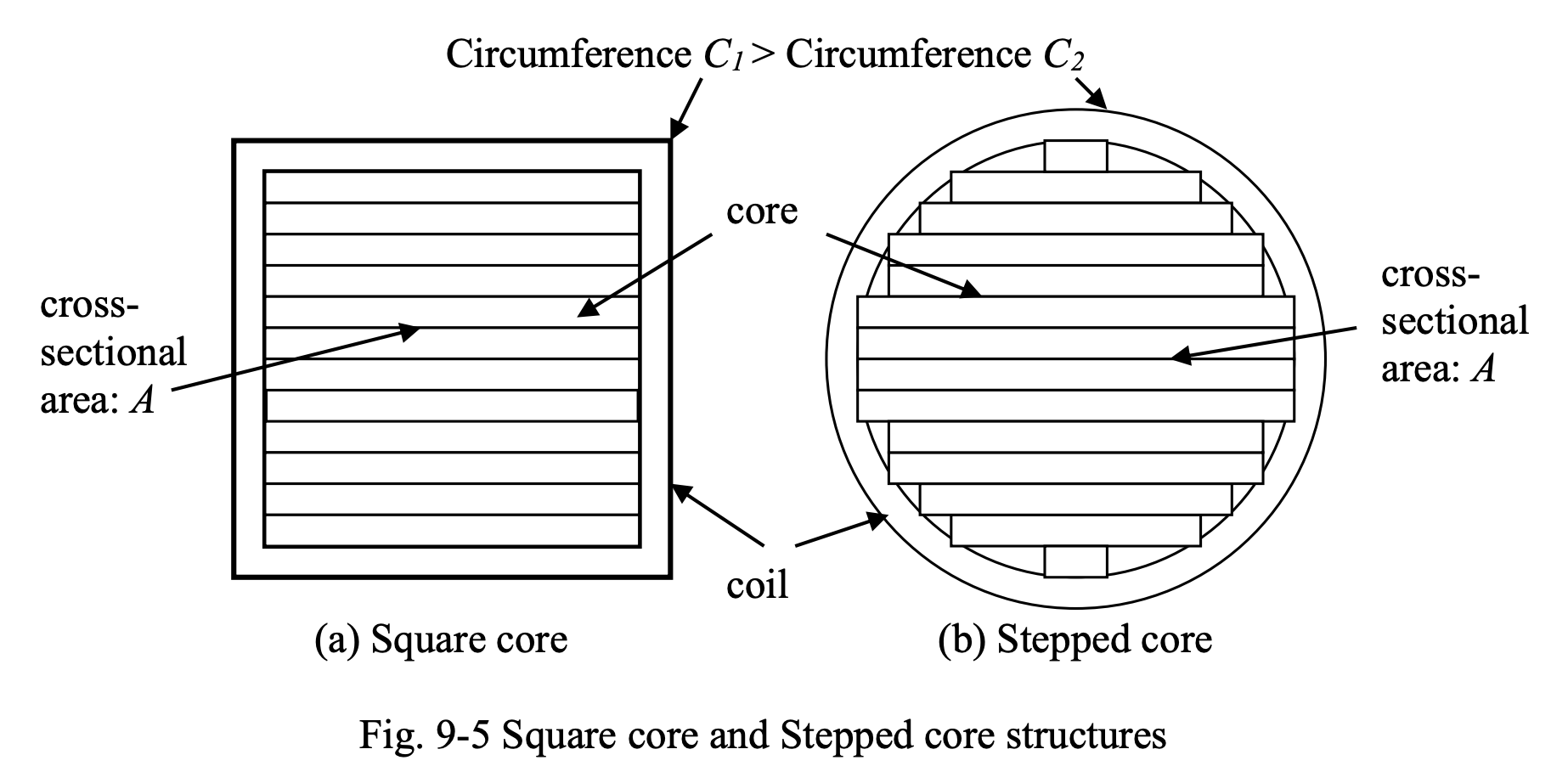
It’s also desirable to reduce the length of the conductor used in the windings as far as possible, as this implies lower copper losses, lower winding resistance. lower transformer cost, lower copper consumption.
Comparing square and circular cross-sections, for a given cross-sectional area, the circumference of a circle will be smaller than that of a square. Therefore, the length of the conductor used in the winding in a circular cross section will be smaller. For practical reasons, in transformers, a circular cross-section is simulated by a stepped cross-section.