A balanced three-phase sinusoidal voltage is comprised of three single-phase sinusoidal voltage sources with the same amplitude and frequency, but phase-shifted by with respect to one another.
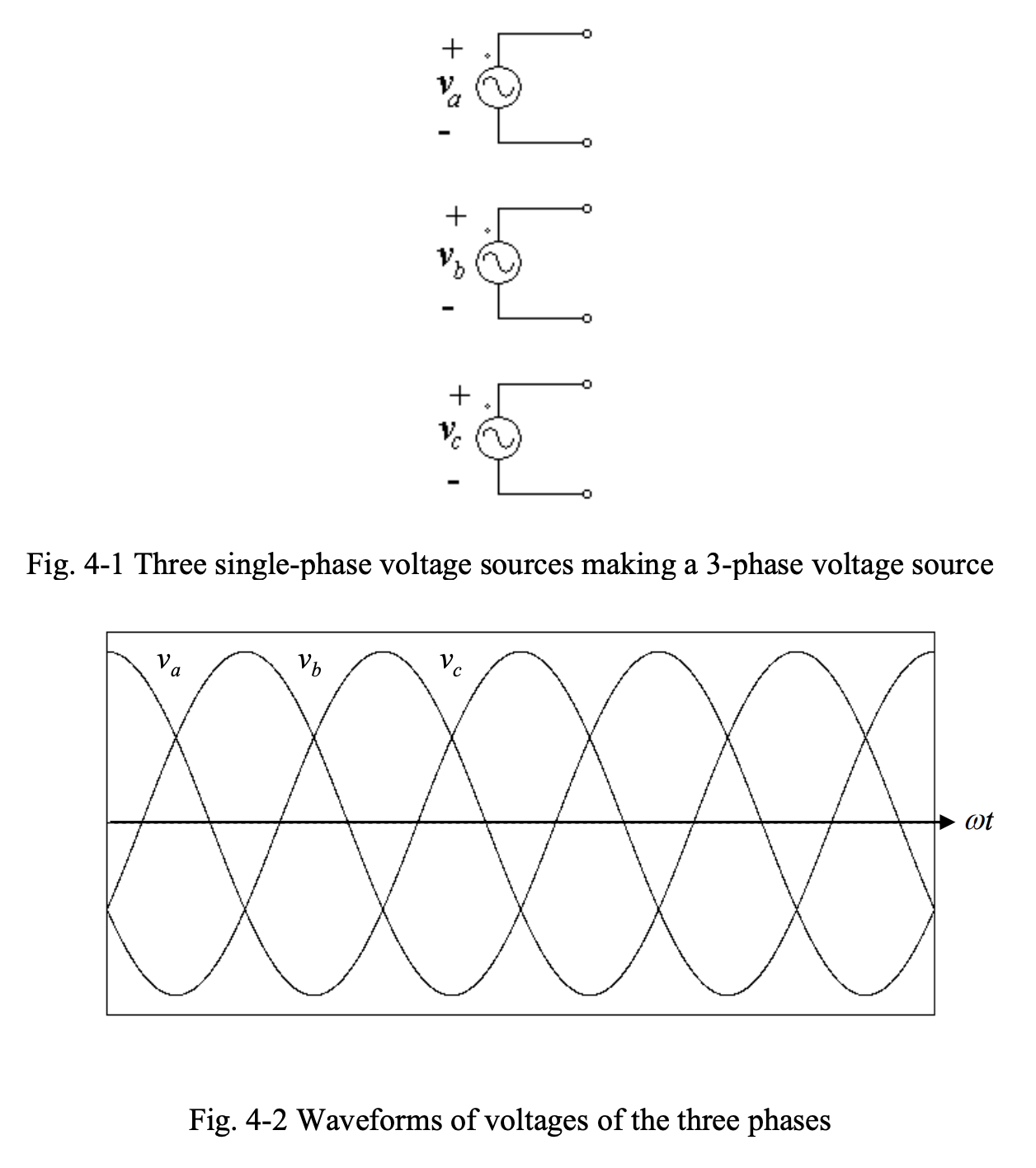
The time and phasor representation of the three single phase voltages are:
- Voltage A:
- Voltage B:
- Voltage C:
Phasor diagram:
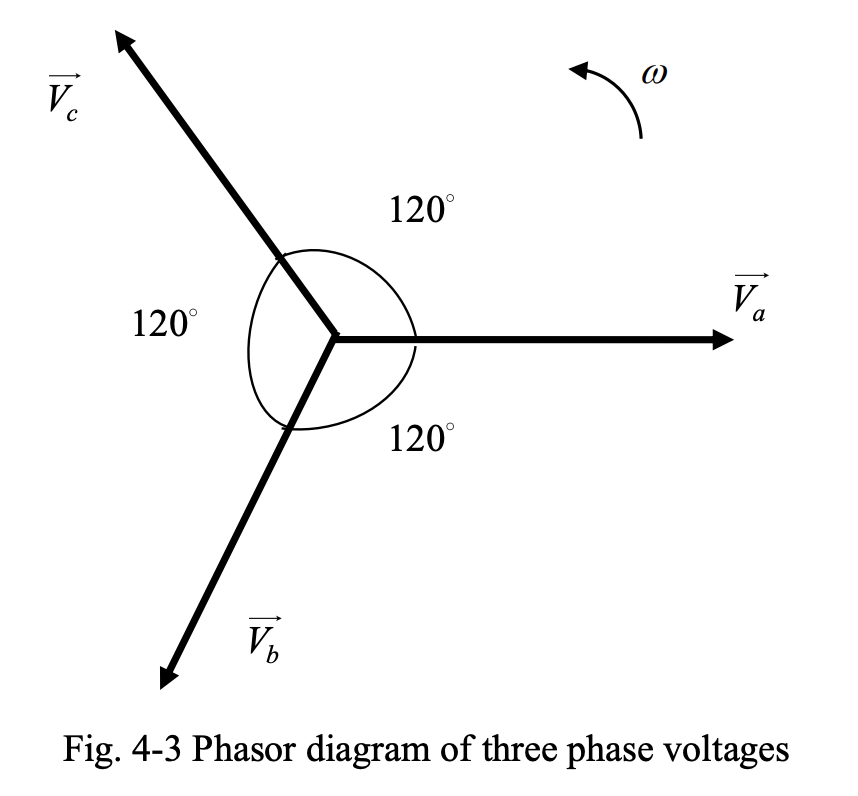
Typically, the voltage of phase is taken as a reference (angle ), and the phase angles of voltages other places are measured with respect to that of phase- voltage.
Phase Sequence
In an ABC or positive sequence, the phasors of the voltages of the three phases rotate in counterclockwise direction (which is considered the positive direction).
- Phase-b voltage follows phase-a voltage, and phase-c voltage follows phase-b voltage.
In an ACB or negative sequence, the phasors of the voltages of the three phases rotate in clockwise direction (which is considered the negative direction).
- Phase-c voltage follows phase-a voltage, and phase-b voltage follows phase-c voltage.
The default sequence is ABC, unless otherwise stated. Changing the sequence from ABC to ACB is used in AC motors to reverse the direction of developed torque and thus the direction of rotation of motor shaft.