Continuous Time
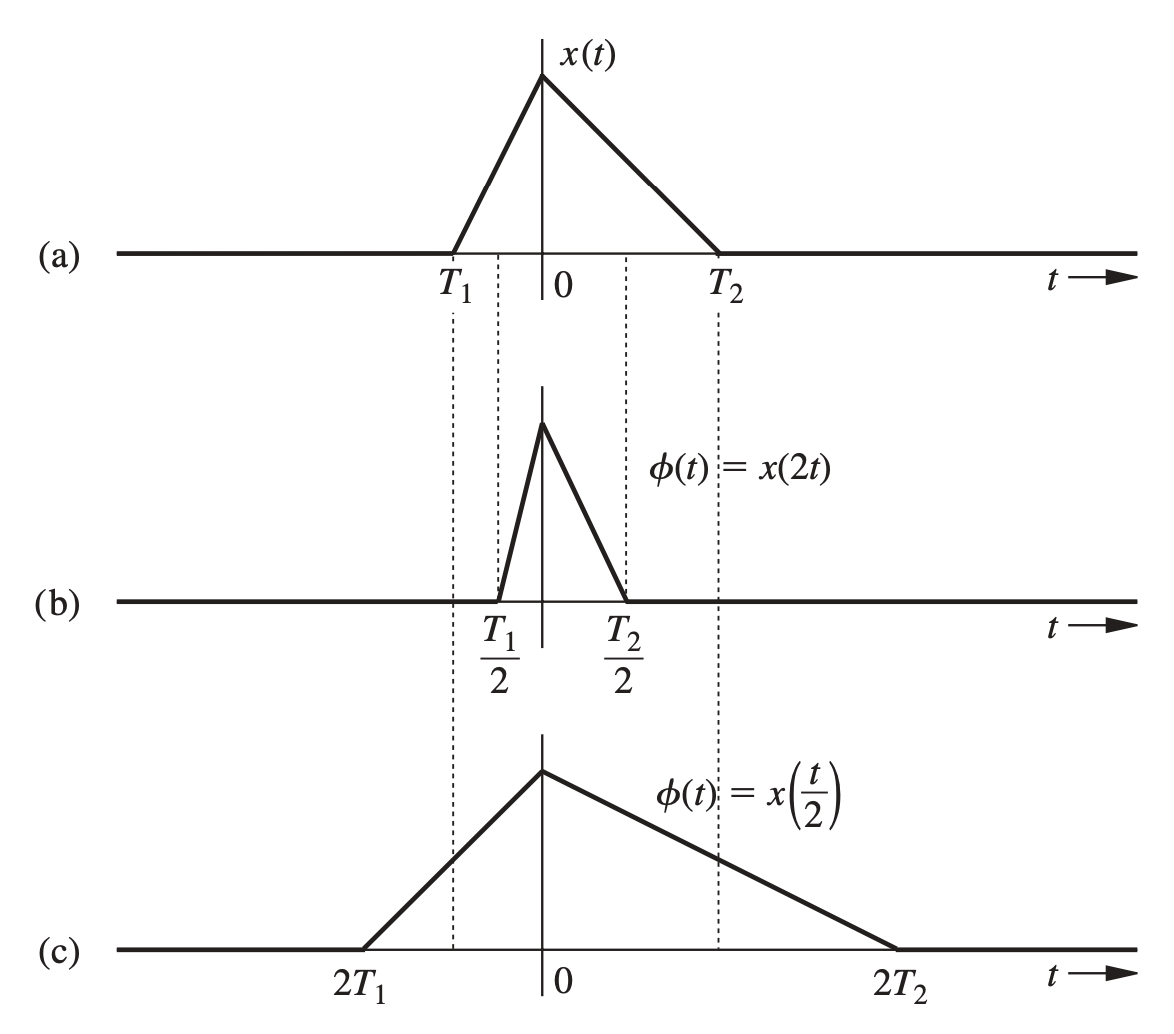
Time scaling refers to the compression or expansion of a signal in time. Basically, we have:
- If , the scaling results in compression.
- If , the scaling results in expansion.
Discrete Time
For compression, we have:
where is an integer factor.
For expansion, we have:
where .
In continuous time, time compression speeds up the signal with no information loss, but in discrete time, time compression downsamples the signal, leading to information loss. For example, if you had 12 discrete points before, now you only have 6.