The CPU does not inherently have any sections of memory that are automatically off limits. Instead, it is the kernel’s job, usually during the boot process, to set up areas of memory that users may or may not access.
- Kernel space: Memory not accessible to protected programs. Not accessible to user-level threads.
- User space: Memory accessible to protected programs and the kernel. Memory that user-level threads can access
The kernel can access both userspace and kernelspace, since it has full control over the computer.
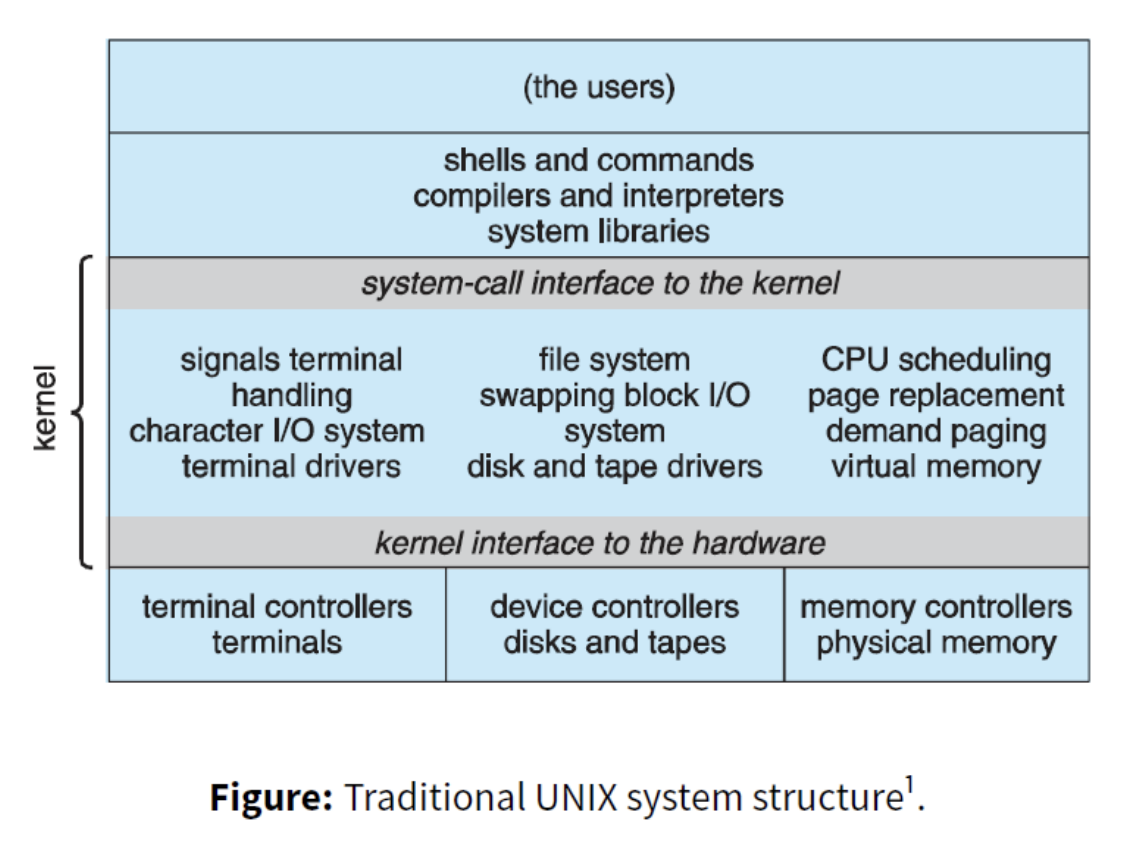
If a user program is running in user space, which is restricted, and hardware is only accessible by the kernel, how do we switch between user space and kernel space? This is done through the System Call interface.