The Cortex M4 has RAM but mainly stores instructions in flash memory, which is slower than RAM. It requires the CPU to wait (???) for flash to be ready before it can start transferring data.
This wait time is dependent on the clock speed and operating voltage, with higher clock speeds and voltages requiring longer wait times (after CPU > 14MHz, there clock speed doesn’t matter). There’s also no real way to speed this up (unlike how RAM can be improved with clock speed) since we’re fundamentally limited by physics.
Cache Solution
The Cortex M4 has two caches, pre-fetch and branch.
Pre-fetch cache
The pre-fetch cache takes advantage of the instruction-decode cycle. Since the CPU has to spend time fetching, decoding and executing (FED cycle), we use those wasted cycles fill a small cache.
The Cortex M4 instruction bus is 128 bytes wide, so whenever instructions are requested, a read of 128 bytes occurs. Since it is a 32-bit microcontroller, this means that a single instruction fetch actually brings in 4 instructions. We can use this to our advantage to avoid flash memory as much as possible. While performing FDE cycles on this 128 byte cache, we can begin the next request, which adds up to a lot of savings over millions of cycles.
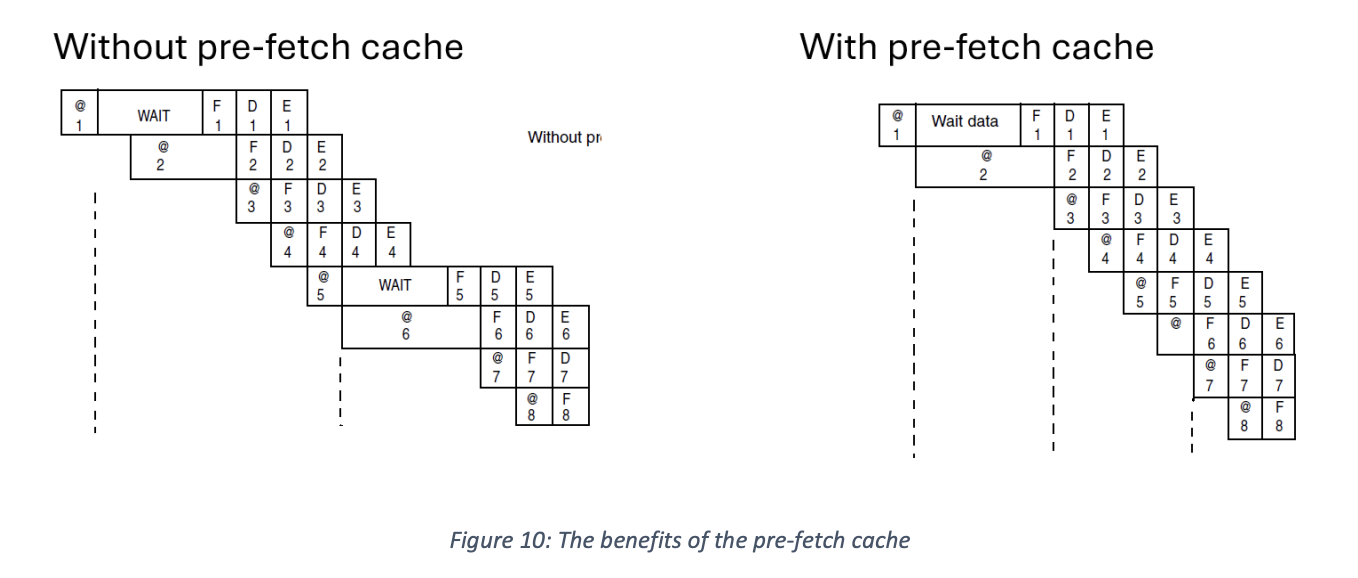
Branch cache
Branch cache is filled from pre-fetch cache and is based on the idea of locality reference (see Cache Optimization); if the compiler is smart, instructions that are executed sequentially will be in contiguous memory addresses. Thus, once we’ve fetched some data we might as well store it in a separate cache – the branch cache. This cache is bigger than the pre-fetch cache (64x128bytes), and it is what is searched first when trying to access an instruction. Since flash is so slow, cache misses don’t significantly affect the processor’s speed. This is especially useful for a microprocessor performing loops.
Data cache
Flash contains both code and data (usually literals). If data is loaded frequently, it ties up the flash memory so code can’t be read. Cortex M4 has a data cache of 8x128 bits.