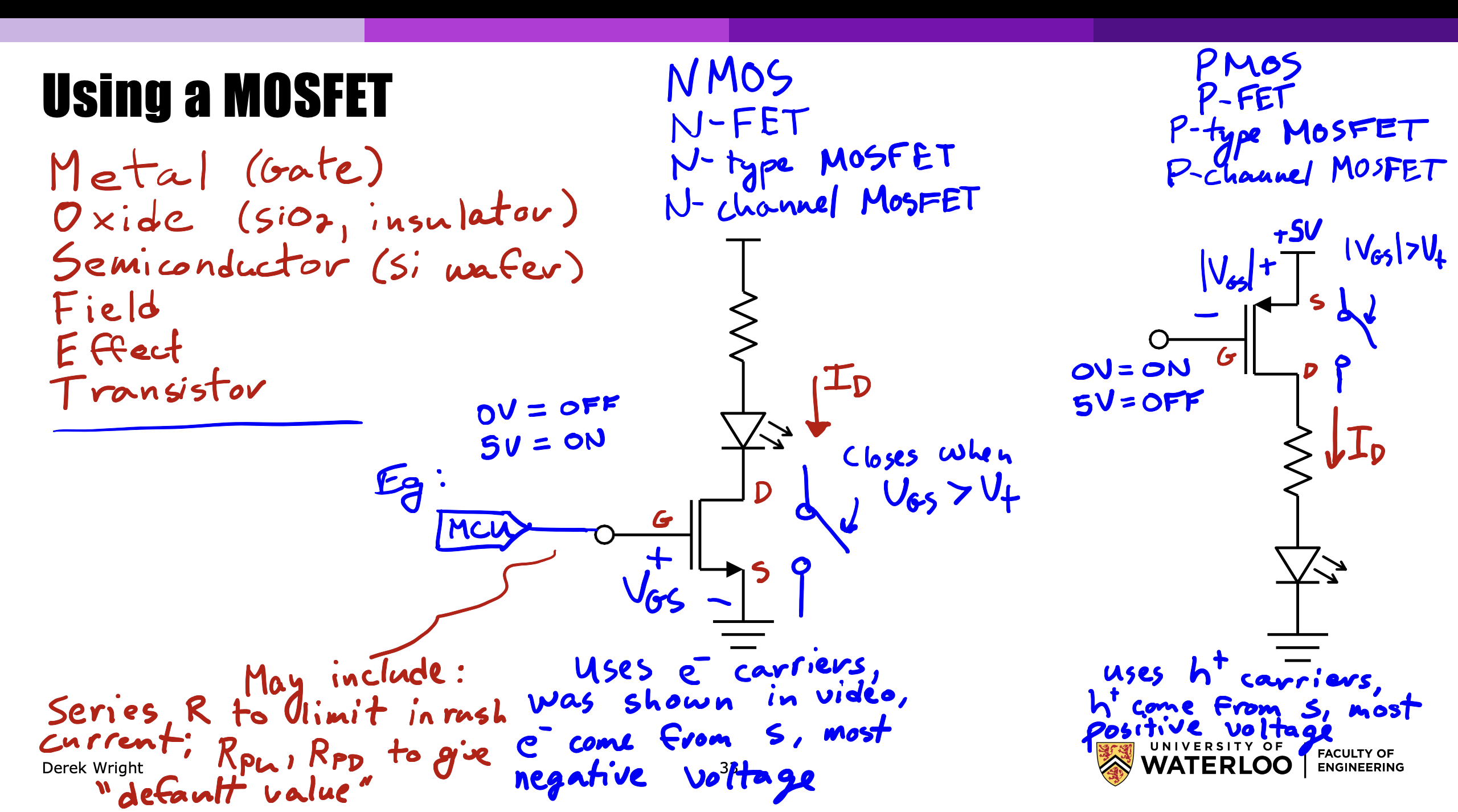
- Metal (Gate)
- Oxide (SiO2, insulator)
- Semiconductor (Si wafer)
- Field
- Effect
- Transistor
NMOS
Also known as N-FET, N-type MOSFET or N-channel MOSFET. This refers to the fact that these use electrons as the charge carrier. Electrons come from source, which is the most negative voltage.
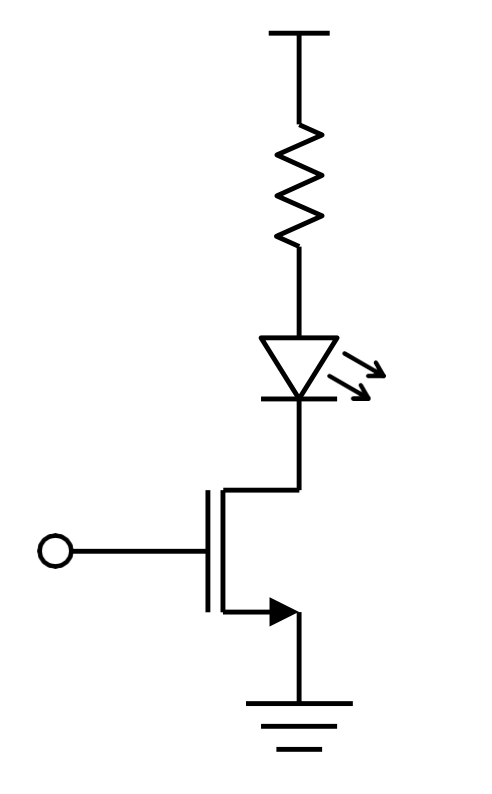
This functions as a switch that is normally open and closes when . When this happens, we get a drain current .
For example, we could have a microcontroller connected to the pin.
- When it outputs , the LED remains off.
- When it outputs , the LED turns on.
A series resistor may be included to limit in rush current.
PMOS
A PMOS uses P-type carriers, which are holes. These carriers come from the source, which is the most positive voltage. In this case, we technically have , but we can just think of it in terms of the difference between the two terminals and use instead.
When is more than the threshold, the drain current activates. The PMOS acts opposite to the NMOS, such that it’s normally ON and turns off when . Thus, we would have:
- = ON
- = OFF
Slide