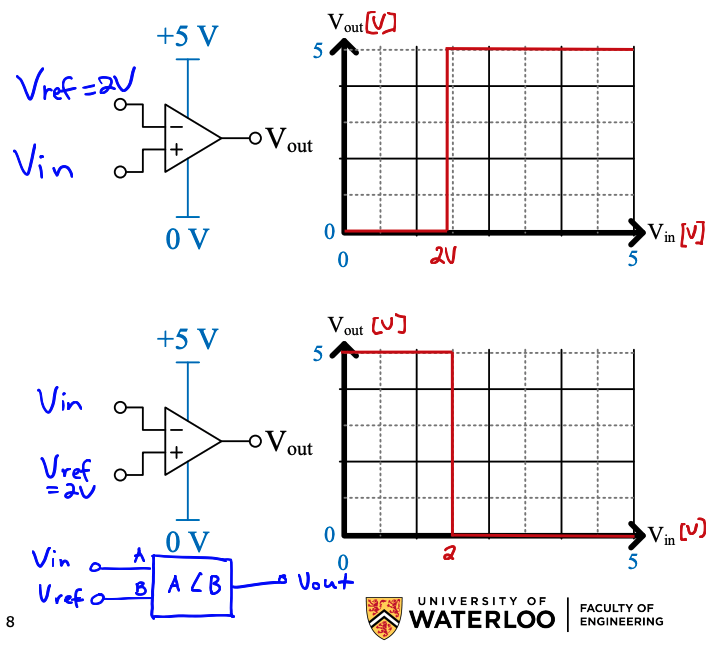
A comparator is kind of like a “greater than or less than” block. It lets us compare two analog signals and give a digital output.
Definition
Example
A digital system with a light sensor for differentiating between night and day.
- Boolean
0= 0 Volts, Boolean1= 5 Volts - Light sensor output voltage exceeds 2V during the day.
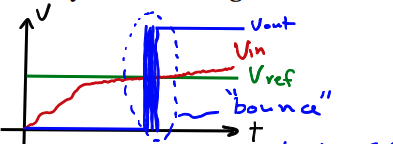
A comparator “slams” any input voltage below the (which is 2V in this case) to zero, and anything above to (5V in this case).
- If is connected to the negative terminal, any input voltage below it is
- “Greater than” operation
- If is connected to the positive terminal, any input voltage above it is
- “Less than” operation