A max pooling layer aggregates information over a spatial range. It acts like a filter but has no weights; given a filter size, it simply returns the maximum value in its field. Note that max pooling layers do not have additional bias or offset values.
Usually, max pooling is applied with the following traits:
- Stride , so that the resulting image is smaller than the input image.
- Filter size , so that the whole image is covered.
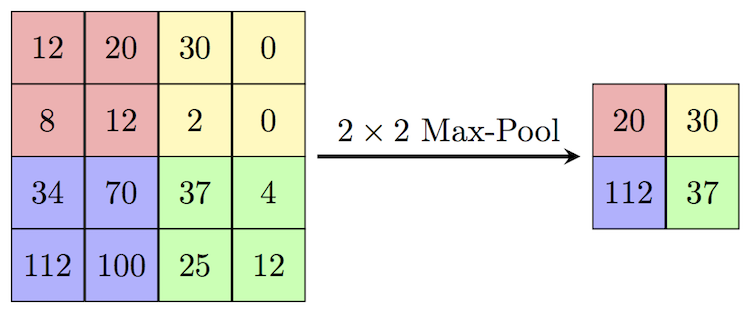
- The above has stride 2 and filter size 2
By applying the max pooling layer, we don’t have to keep track of the precise location of a pattern; this helps our filters to learn to recognize patterns independent of their location.
Consider a max pooling layer with . This would map a image to a image.