Motor equation:
Pole at:
% set time step
time_to_plot = 2;
T = 0.005;
%% Continuous Time
num = [-107];
denom = [1 50.7614 0];
cont_TF = tf(num, denom);
G = c2d(cont_TF, T);
pole(G)
zero(G)
zpk(G)
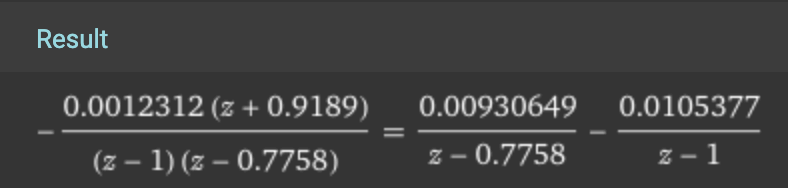
-0.0012312 (z+0.9189)
---------------------
(z-1) (z-0.7758)
Partial fraction decomposition:
Columns 1 through 5
-0.2137 - 0.0912i -0.2137 + 0.0912i 0.0974 - 0.3139i 0.0974 + 0.3139i 0.3984 - 0.0575i
Columns 6 through 10
0.3984 + 0.0575i 0.3216 + 0.3355i 0.3216 - 0.3355i -0.0377 + 0.5182i -0.0377 - 0.5182i
Columns 11 through 15
-0.4197 + 0.3845i -0.4197 - 0.3845i -0.6142 + 0.0282i -0.6142 - 0.0282i -0.5418 - 0.3721i
Columns 16 through 20
-0.5418 + 0.3721i -0.2461 - 0.6522i -0.2461 + 0.6522i 0.1564 - 0.7180i 0.1564 + 0.7180i
Columns 21 through 25
0.5318 - 0.5578i 0.5318 + 0.5578i 0.7722 - 0.2274i 0.7722 + 0.2274i 0.8186 + 0.1787i
Columns 26 through 30
0.8186 - 0.1787i 0.6664 + 0.5584i 0.6664 - 0.5584i 0.3569 + 0.8262i 0.3569 - 0.8262i
Stiction with Ball and Beam
- Upward (higher than before because we need to fight gravity): -0.48
- Downward (lower than before because gravity is helping us): -0.05
Part E:
When ball is at 0, sensor reading = 310 When ball is at end, sensor reading = 630 Beam length = 41.7
The motor rotates the motor gear with radius . The gear pulls a lever arm of length attached to the beam. A small rotation of the motor (angle ) moves the end of the lever by an arc length .
The displacement causes the lever to rotate the beam, which is given by:
So the ratio is
Therefore,