Goal: Find a lower order polynomial for testing if is Schur, since lower order is easier to check.
Approach: Cancel out from and then divide by to reduce the order by at least one.
First, let us define:
For example:
We can do our aforementioned goal of reducing the order by at least one. To do so, we take the difference between and a scaled version of :
At , we have , so the constant term is zero. Thus,
So:
Thus, is order .
Lemma
Suppose . Then is Schur if and only if is Schur.
Then, define . We create a sequence by repeated application of this lemma
where the order is decreasing:
We stop when we reach the order 1 polynomial . This has the form , so it only has one root at .
This is equivalent to saying
- For the special case of a 1st order polynomial, the polynomial is Schur if and only if . (This makes sense as the root is at so needs to be smaller than for it to be in the unit circle).
Jury Test Algorithm
Given for some .
Check if .
- If not, then is not Schur (lemma from class).
- Then is not Schur (lemma from class).
- Then, is not Schur (lemma from class).
- (presumably only made it to this step if for )
- If yes, does ?
- If no, set and repeat
- are from
- is from reversing coefficients in
- If yes, is Schur
- If no, set and repeat
For each , we need to check if .
- Assume ; if not, use instead.
Then:
Jury Test Theorem
Assume for . If not, use instead.
Then, is Schur if and only if the leading coefficients of for all are positive.
This leads to a tabular method for testing whether is Schur.
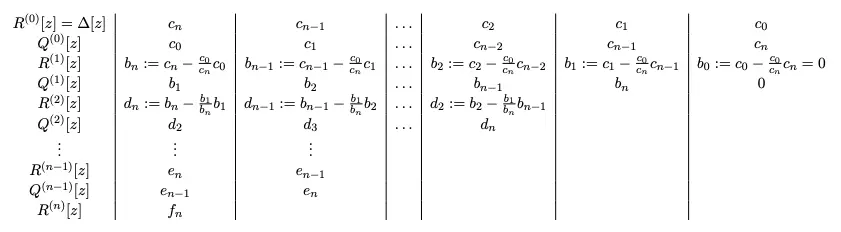
Then is Schur if and only if the coefficients in the first column (i.e., the leading coefficients) are positive for each .
This is if and only if and .
Theorem: Jury Test
Assume (if not, use ).
Then, is Schur if and only if
We either check or go to .
Example
Take . Then, we have:

where we have:
and
Since , , and , is Schur [theorem from class].
Note: To see that it is equivalent to check that as .
Tutorial Example
For a discrete time system, determine the range of that stabilizes the CL system.
Then, the closed-loop polynomial is:
- The first term is stable (root at -0.5), but we need to check if the second term is Schur
The Jury Test:
Then:
Which gives , since we must have .
Then:
which gives
Then:
so:
to get , we need
This is not possible; no value of would allow the system to be CL stable.