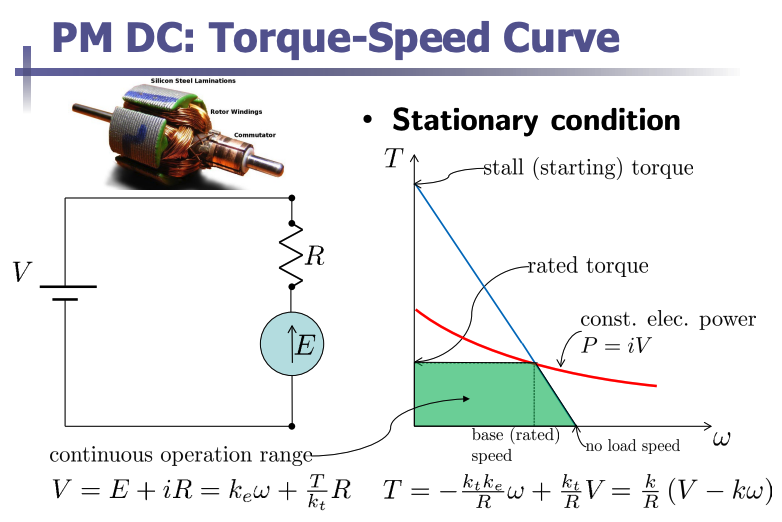
We can model permanent magnet (PM) DC motors as:
where is the supply voltage, is the back EMF, is the current through the armature, is the armature resistance, is the generated torque, and is the angular velocity.
The torque-speed of the motor can be derived as:
This equation shows that torque decreases linearly with increasing speed for a constant supply . The negative slope indicates that torque decreases as speed increases.