Lubrication:
- Reduces friction and wear
- Prevents corrosion
- Dissipates heat
- Dispels contaminants and moisture
Main considerations for design of sealing:
- Lubricant retention
- Contaminant exclusion
- Rotational speed
- Pressure differential
Lubrication
There are two main types of lubrication:
- Grease lubrication: Usually used for lifetime lubrication (with bearing shield/seals). Shielded type bearings (ZZ or DD type)
- Oil lubrication: Usually for high speeds or continuous runs (e.g. drive trains). Open type bearings (no suffix).
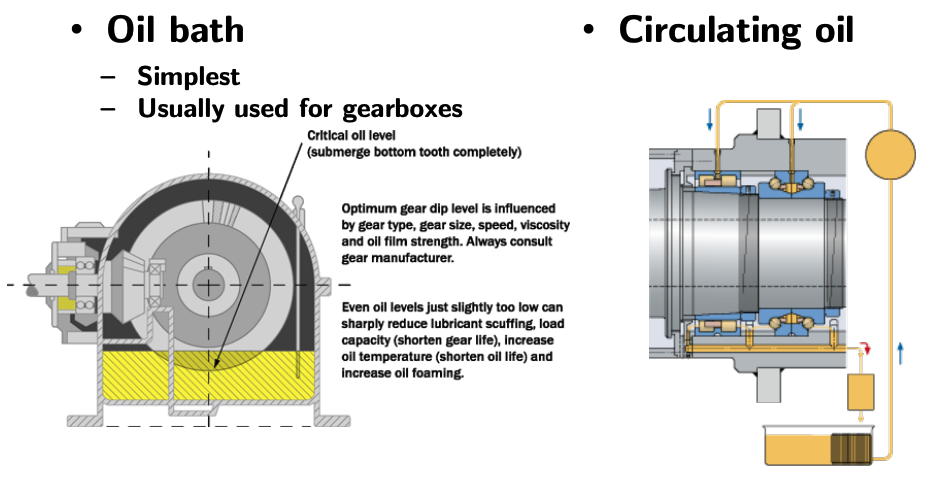
Oil Lubrication for Drive Trains
Either use oil bath (simplest, usually used for gear boxes) or circulating oil.
Bearing Sealing
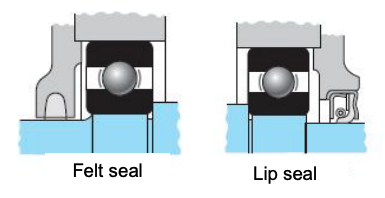
External seal designs include:
- Felt seals (contact)
- Lip seals (contact)
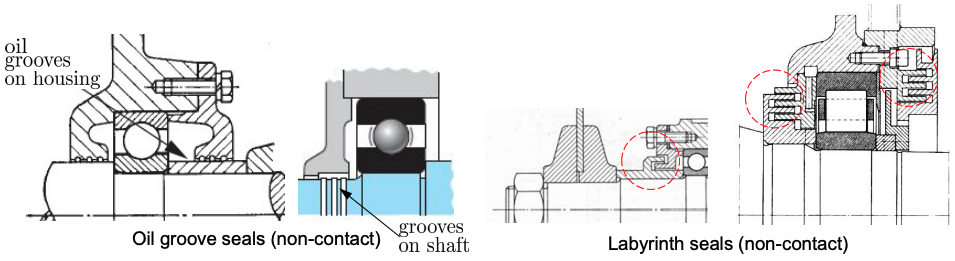
- Oil groove seals (non-contact)
- Labyrinth seals (non-contact)
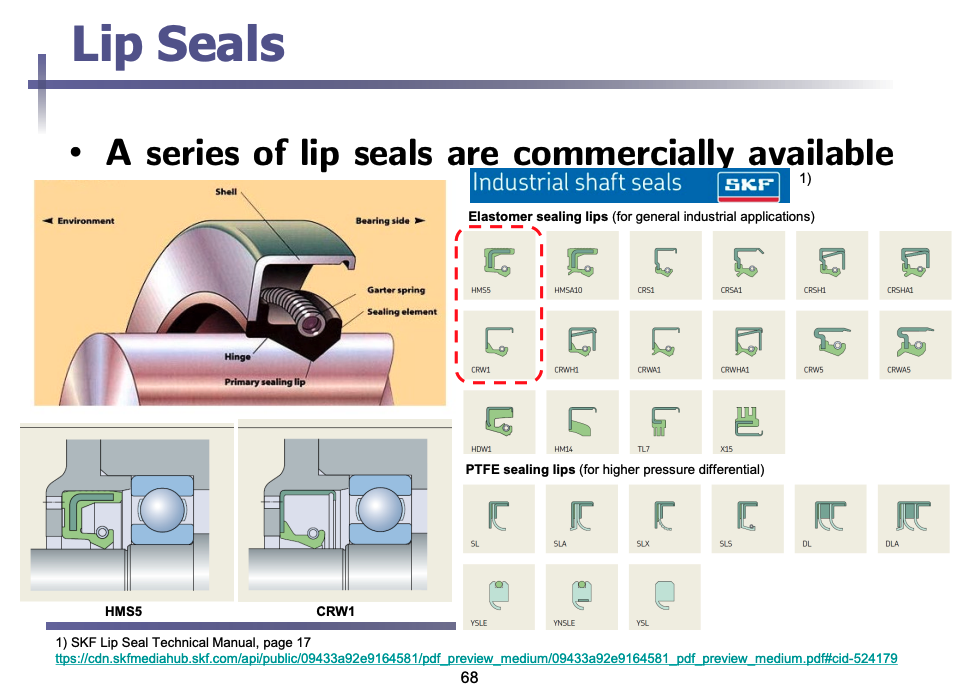
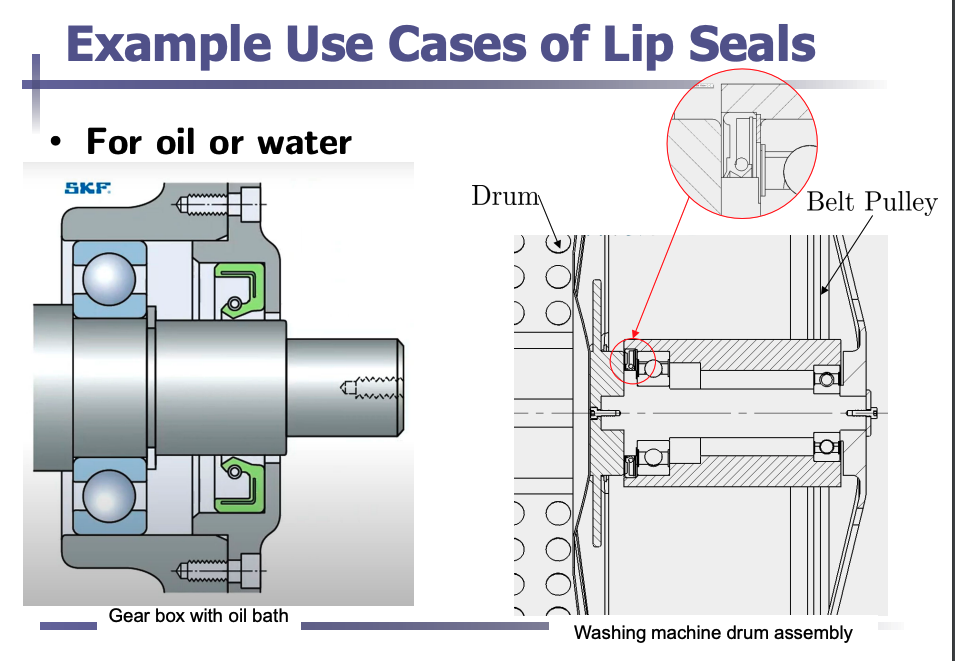
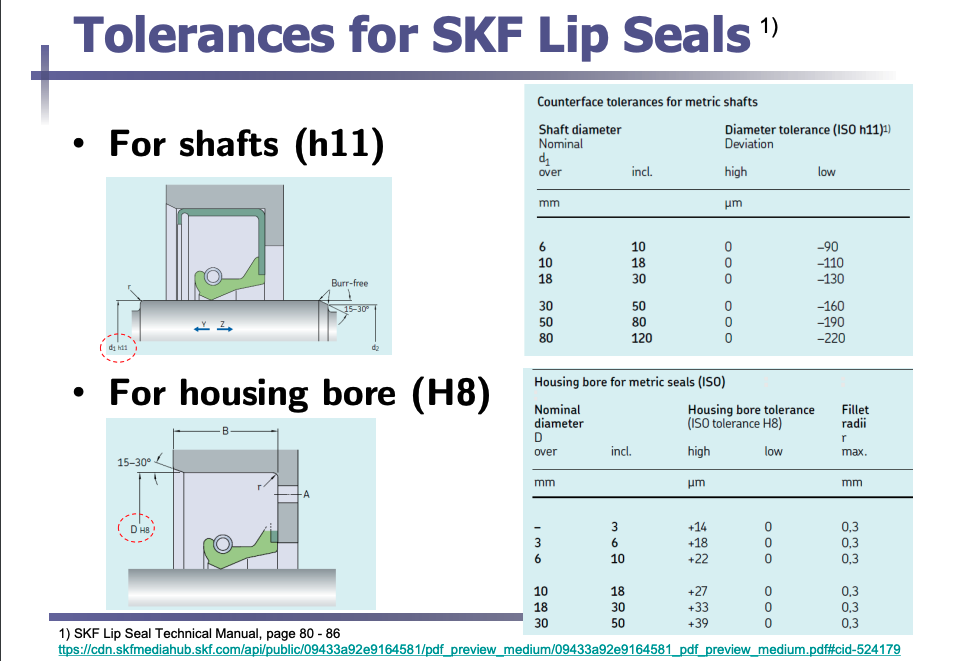
Lip seals
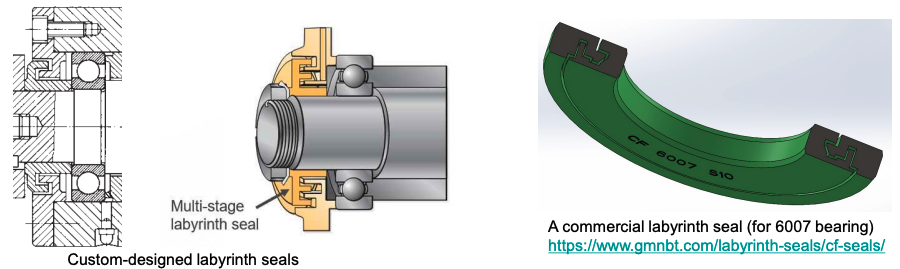
Labyrinth Seals
- Non-contact, used for high-speed machines
- Milling spindles, table saws, etc.
- Contain oil and grease (not water) through centrifugal force
- Inner and outer rings support respective parts of the mated bearing
- Either custom-design or off-the-shelf products
- Typical gap size: 0.2 to 0.5 mm