Steady, incompressible, plane, two-dimensional flow represents one of the simplest types of flow of practical importance. By plane, two-dimensional flow we mean that there are only two velocity components, such as u and when the flow is considered to be in the – plane.
The continuity equation for an incompressible fluid in 3D is expressed as:
For 2D flows, this simplifies to:
This possible to relate and using a single function ?
If has continuous second-order derivatives:
This definition automatically satisfies the continuity equation.
What exactly is ?
On a curve on which , we would have
Thus, defines a streamline.
What is the meaning of the value of the value of ?
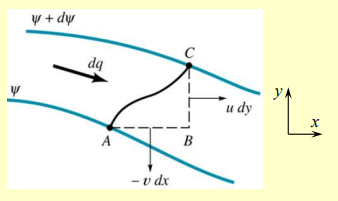
Consider the difference between difference in the stream function values between two streamlines:
Substituting the definitions of and :
Integrating from one streamline to another:
The difference in values is equal to the flow rate between those two streamlines. This is a powerful result because it allows us to compute mass flow rates just by knowing the stream function!