Horizontal
In a horizontal pipe, the fluid element analysis assumes no gravitational influence in the flow direction
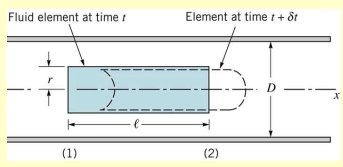
The force balance simplifies to
where is the pressure difference across the pipe length , is the shear stress, is the radius of the fluid element, and is the length of the fluid element
The velocity profile for fully developed laminar flow remains parabolic, as derived when we did laminar flow fluid element analysis:
Inclined
For a pipe inclined at an angle , the gravitational component along the pipe’s axis introduces an additional force term.
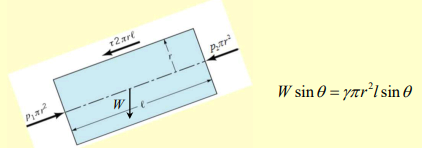
In this case, the force balance equation becomes
We now can find the effective pressure drop considering gravity as:
so that we can simplify the expression to . We can also write:
Velocity Volumetric Mass Flow Rate
The average velocity () in both cases is calculated by integrating the velocity profile over the pipe’s cross-sectional area:
Using the regular for the inclined case:
The volumetric flow rate is the product of average velocity and the cross-sectional area of the pipe: