For a crank-slider linkage, the problem set-up first requires that we know:
- Angular and linear accelerations (determined through kinematic analysis)
- Masses of links
- Position information (link lengths, link positions, location of center of gravity for each link)
- Mass moment of inertia with respect to CG, , for each link
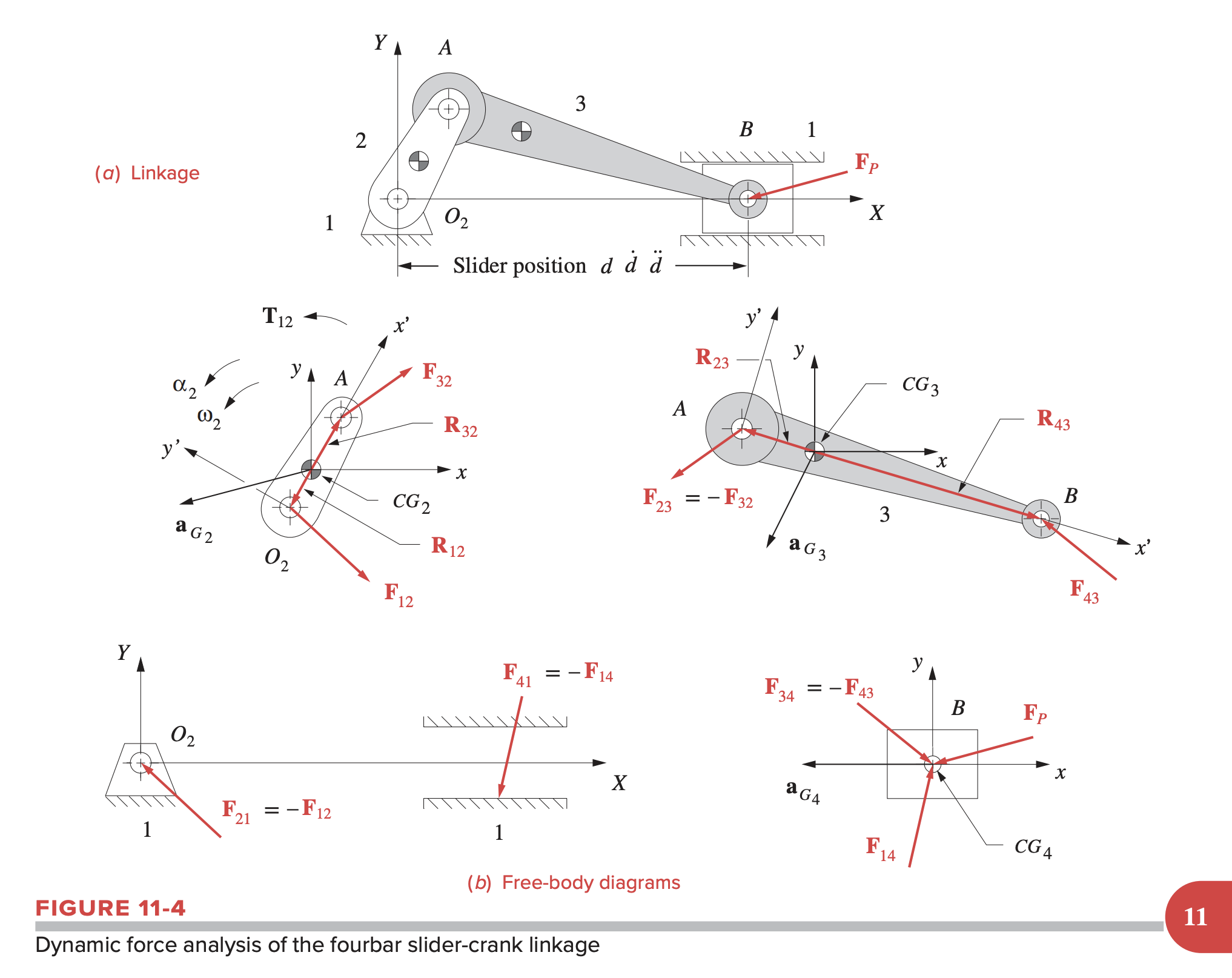
We then write out the forces and moments for each link.
Link 2:
Link 3:
Link 4:
Considering that we have a crank-slider means:
We need to consider the friction force at the interface:
Signs will be opposite of slider velocity, .
Examining friction force:
where the function returns the sign of .
Considering acceleration specifics regarding Link 4 and friction force, the Link 4 equations become:
This finally gives us a system with 8 unknowns:
We can then take the inverse of the matrix to solve: