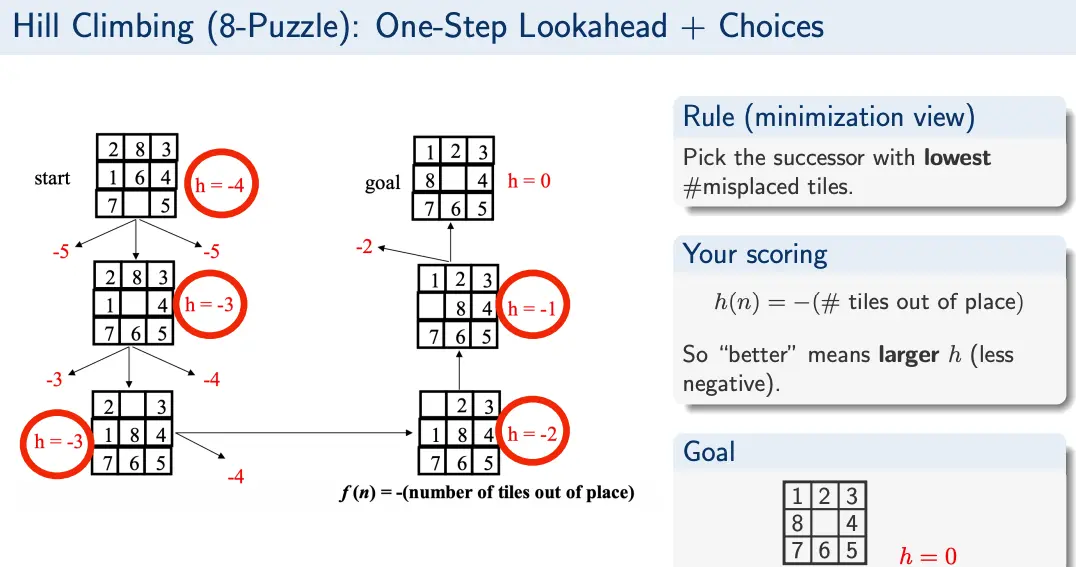
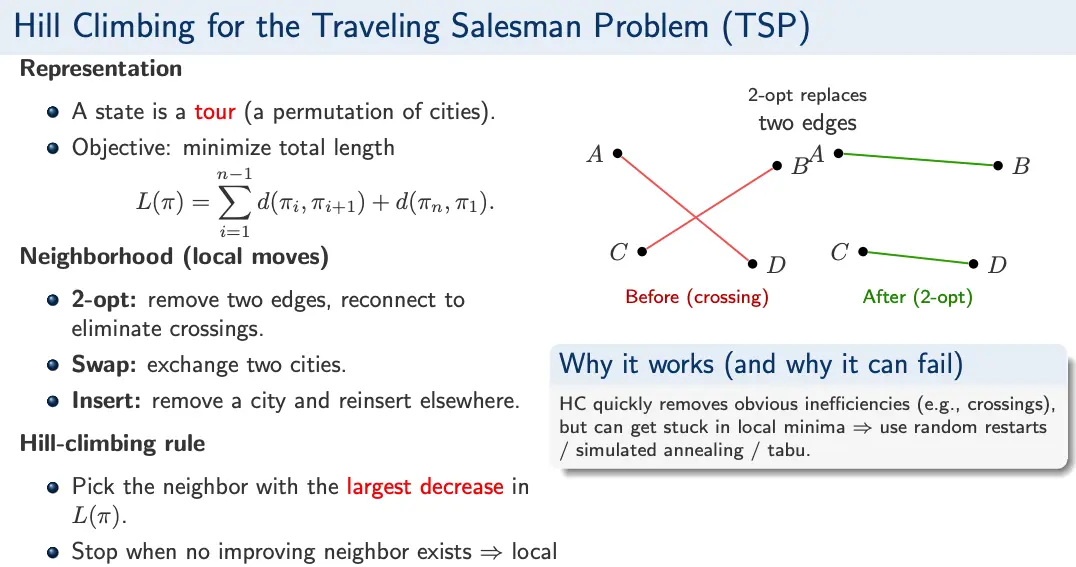
Hill-climbing is a local-neighborhood exploration search algorithm. We start with an arbitrary solution, then search for a better one by incrementally changing a single element of the solution. Successors of anode are sorted by heuristic value.
- If there exists a successors of the current state such that
- , and
- for all successors of
- then move from to
- Otherwise, halt at .
Example
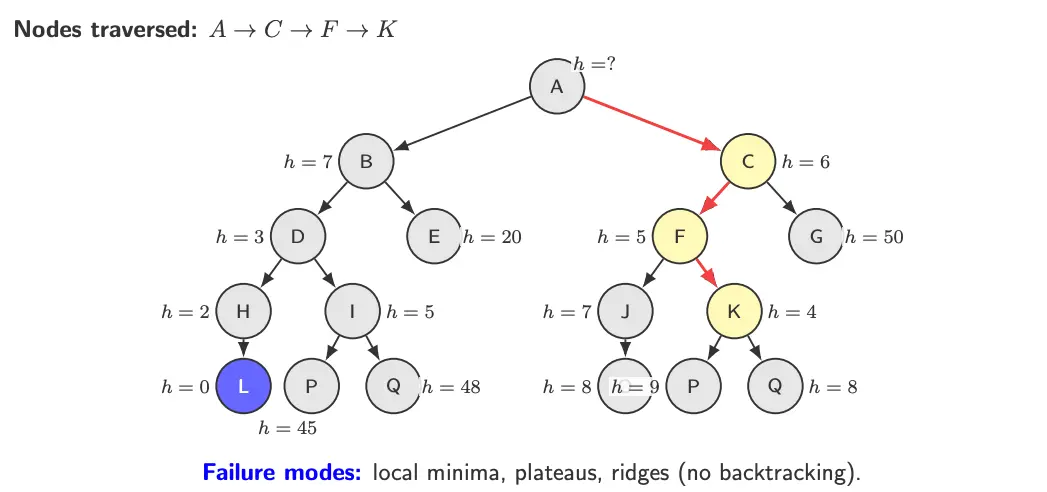
Comparisons
Hill climbing vs. Greedy Best-First Search:
- Both use heuristic to prefer better states
- Hill climbing does not keep a frontier and does not backtrack or jump to an alternative path (it does not remember where it has been)
Hill climbing vs. Beam Search:
- Equivalent to beam search with beam width (keep only one candidate at each step)

In the above example, Greedy Best-First Search would go . That is, it uses global frontier information and can recover from local minima.
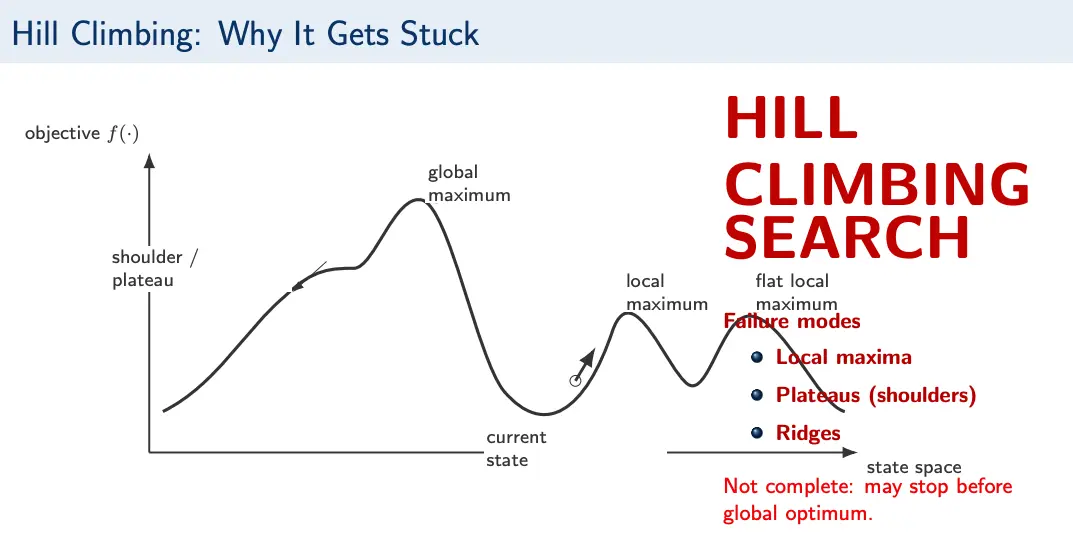
Limitations
The key limitation of hill climbing search is that it may terminate at local minima, plateaus, or ridges.
Applications