Helical gears have gears inclined to the axis of rotation. Helical gears can be used for the same applications as spur gears and are not as noisy, because of the more gradual engagement of the teeth during meshing.
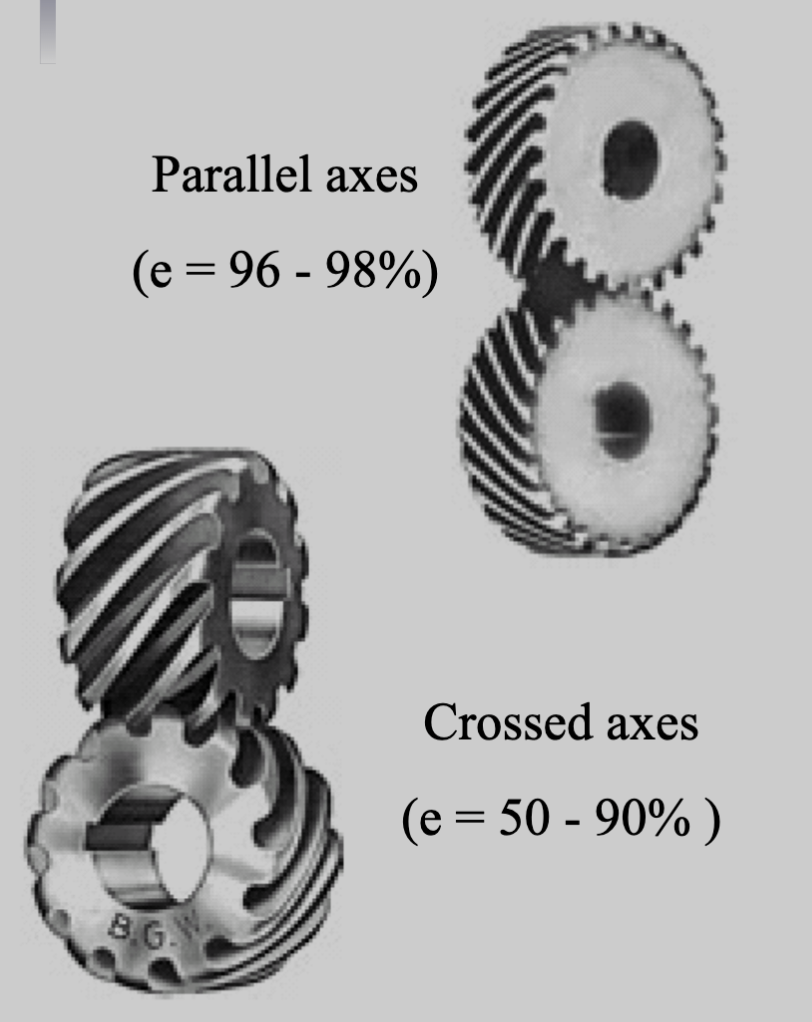
The inclined tooth also develops thrust loads and bending couples, which are not present with spur gearing. Sometimes helical gears are used to transmit motion between nonparallel shafts.
Some key points:
- Teeth not parallel to axis
- More expensive than spur
- Quieter than others
- Axial force component
- Parallel or crossed axes
- Stronger tooth section
- Harder to disengage
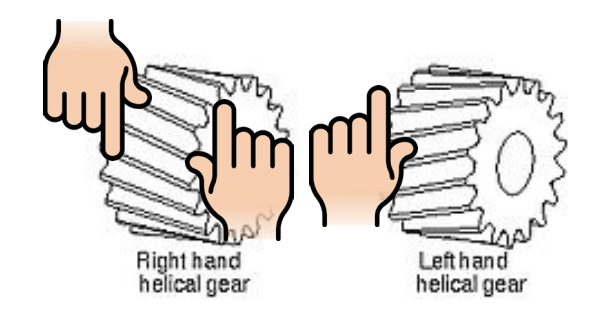
Right vs. Left Handed
- Helical gears are mated with opposite handedness
- By definition, right-handed gear means that “the teeth twist clockwise as they recede from an observer looking along the axis”