Geometric irregularities often occur in members. Some possible irregularities:
- Shoulders on rotating shafts
- Key slots in shafts
- Bolts with heads and screw threads
- Flange couplings, gears, and pulleys attached to shafts by keys in keyways
- Tool marks, holes, notches, grooves or threads
A discontinuity in a machine part is an irregularity that alters the stress distribution in the neighborhood of the discontinuity, so that the elementary stress equations no longer describe the state of stress in the part at these locations. Such discontinuities are called stress raisers, and the regions in which they occur are called areas of stress concentration.
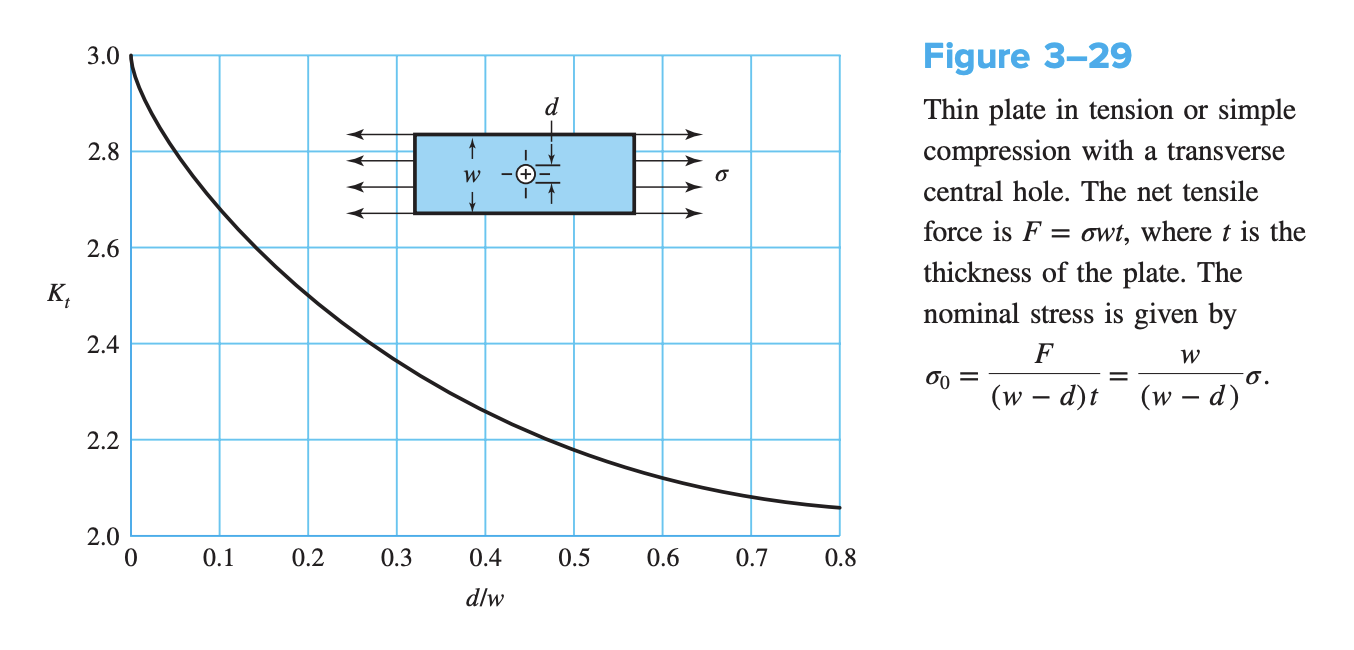
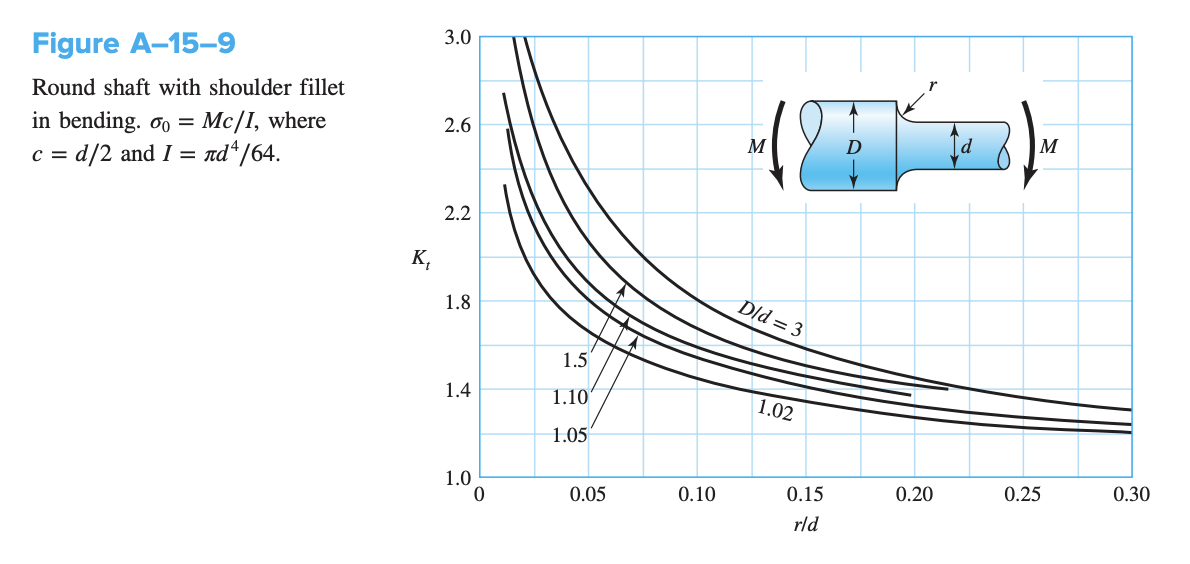
A theoretical or geometric stress-concentration factor or is used to relate the actual maximum stress at the discontinuity to the nominal stress:
where is used for normal stresses and for shear stresses. The nominal stress or is the stress calculated by using the elementary stress equations and the net area/net cross-section.
Graphs are available for standard configuration, that expressed and as a result of various properties of the irregularity.