Power electronics is the art of converting the electric power available from a source to that required by a load (i.e., matching the properties of the source with the requirements of the load).
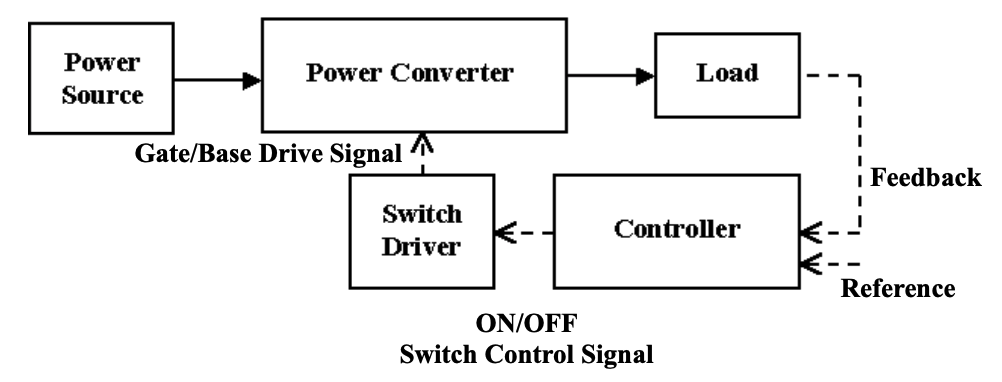
The conversion is performed by a power converter composed of semiconductor devices (diodes, switches), energy storage elements (inductors, capacitors), and isolation transformers. A closed-loop control system makes sure the output of interest follows the corresponding reference. The figure below shows the block diagram of a typical power electronic system.